<div align="center">
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asyml/forte/master/docs/_static/img/logo_h.png"><br><br>
</div>
-----------------
<p align="center">
<a href="https://github.com/asyml/forte/actions/workflows/main.yml"><img src="https://github.com/asyml/forte/actions/workflows/main.yml/badge.svg" alt="build"></a>
<a href="https://codecov.io/gh/asyml/forte"><img src="https://codecov.io/gh/asyml/forte/branch/master/graph/badge.svg" alt="test coverage"></a>
<a href="https://asyml-forte.readthedocs.io/en/latest/"><img src="https://readthedocs.org/projects/asyml-forte/badge/?version=latest" alt="documentation"></a>
<a href="https://github.com/asyml/forte/blob/master/LICENSE"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/license-Apache%202.0-blue.svg" alt="apache license"></a>
<a href="https://gitter.im/asyml/community"><img src="http://img.shields.io/badge/gitter.im-asyml/forte-blue.svg" alt="gitter"></a>
<a href="https://github.com/psf/black"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/code%20style-black-000000.svg" alt="code style: black"></a>
</p>
<p align="center">
<a href="#installation">Download</a> •
<a href="#quick-start-guide">Quick Start</a> •
<a href="#contributing">Contribution Guide</a> •
<a href="#license">License</a> •
<a href="https://asyml-forte.readthedocs.io/en/latest">Documentation</a> •
<a href="https://aclanthology.org/2020.emnlp-demos.26/">Publication</a>
</p>
**Bring good software engineering to your ML solutions, starting from Data!**
**Forte** is a data-centric framework designed to engineer complex ML workflows. Forte allows practitioners to build ML components in a composable and modular way. Behind the scene, it introduces [DataPack](https://asyml-forte.readthedocs.io/en/latest/notebook_tutorial/handling_structued_data.html), a standardized data structure for unstructured data, distilling
good software engineering practices such as reusability, extensibility, and flexibility into
ML solutions.
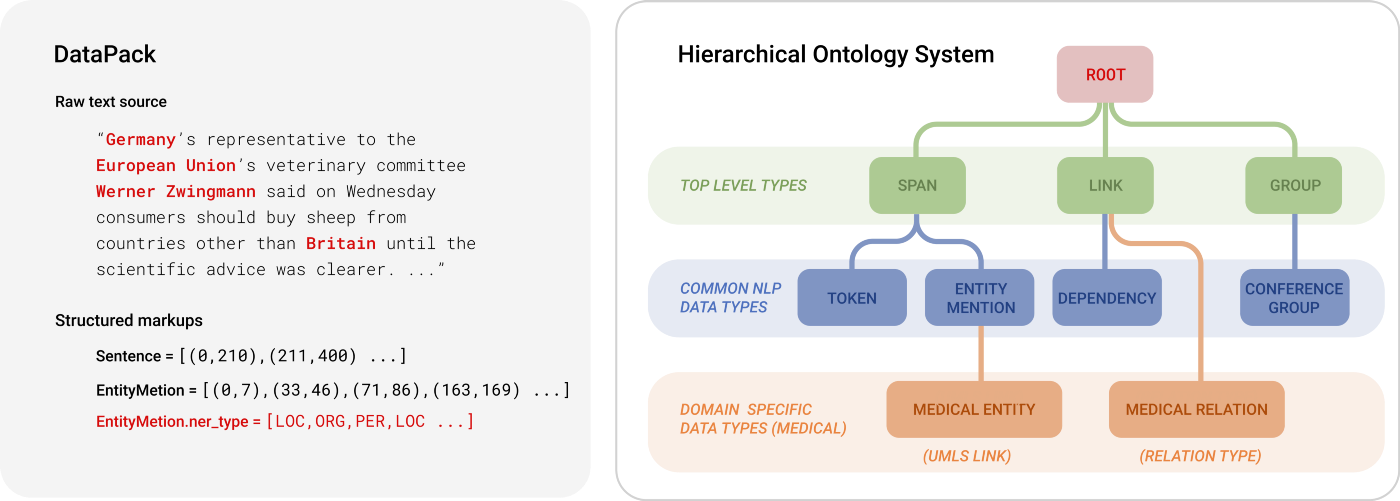
DataPacks are standard data packages in an ML workflow, that can represent the source data (e.g. text, audio, images) and additional markups (e.g. entity mentions, bounding boxes). It is powered by a customizable data schema named "Ontology", allowing domain experts to inject their knowledge into ML engineering processes easily.
## Installation
To install the released version from PyPI:
```bash
pip install forte
```
To install from source:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/asyml/forte.git
cd forte
pip install .
```
To install some forte adapter for some existing [libraries](https://github.com/asyml/forte-wrappers#libraries-and-tools-supported):
Install from PyPI:
```bash
# To install other tools. Check here https://github.com/asyml/forte-wrappers#libraries-and-tools-supported for available tools.
pip install forte.spacy
```
Install from source:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/asyml/forte-wrappers.git
cd forte-wrappers
# Change spacy to other tools. Check here https://github.com/asyml/forte-wrappers#libraries-and-tools-supported for available tools.
pip install src/spacy
```
Some components or modules in forte may require some [extra requirements](https://github.com/asyml/forte/blob/master/setup.py#L45):
* `pip install forte[data_aug]`: Install packages required for [data augmentation modules](https://github.com/asyml/forte/tree/master/forte/processors/data_augment).
* `pip install forte[ir]`: Install packages required for [Information Retrieval Supports](https://github.com/asyml/forte/tree/master/forte/processors/ir/)
* `pip install forte[remote]`: Install packages required for pipeline serving functionalities, such as [Remote Processor](https://github.com/asyml/forte/processors/misc/remote_processor.py).
* `pip install forte[audio_ext]`: Install packages required for Forte Audio support, such as [Audio Reader](https://github.com/asyml/forte/blob/master/forte/data/readers/audio_reader.py).
* `pip install forte[stave]`: Install packages required for [Stave](https://github.com/asyml/forte/blob/master/forte/processors/stave/stave_processor.py) integration.
* `pip install forte[models]`: Install packages required for [ner training](https://github.com/asyml/forte/blob/master/forte/trainer/ner_trainer.py), [srl](https://github.com/asyml/forte/tree/master/forte/models/srl), [srl with new training system](https://github.com/asyml/forte/tree/master/forte/models/srl_new), and [srl_predictor](https://github.com/asyml/forte/tree/master/forte/processors/nlp/srl_predictor.py) and [ner_predictor](https://github.com/asyml/forte/tree/master/forte/processors/nlp/ner_predictor.py)
* `pip install forte[test]`: Install packages required for running [unit tests](https://github.com/asyml/forte/tree/master/tests).
* `pip install forte[wikipedia]`: Install packages required for reading [wikipedia datasets](https://github.com/asyml/forte/tree/master/forte/datasets/wikipedia).
* `pip install forte[nlp]`: Install packages required for additional NLP supports, such as [subword_tokenizer](https://github.com/asyml/forte/tree/master/forte/processors/nlp/subword_tokenizer.py) and [texar encoder](https://github.com/asyml/forte/tree/master/forte/processors/third_party/pretrained_encoder_processors.py)
* `pip install forte[extractor]`: Install packages required for extractor-based training system, [extractor](https://github.com/asyml/forte/blob/master/forte/data/extractors), [train_preprocessor](https://github.com/asyml/forte/tree/master/forte/train_preprocessor.py), [tagging trainer](https://github.com/asyml/forte/tree/master/examples/tagging/tagging_trainer.py), [DataPack dataset](https://github.com/asyml/forte/blob/master/forte/data/data_pack_dataset.py), [types](https://github.com/asyml/forte/blob/master/forte/data/types.py), and [converter](https://github.com/asyml/forte/blob/master/forte/data/converter).
## Quick Start Guide
Writing NLP pipelines with Forte is easy. The following example creates a simple pipeline that analyzes the sentences, tokens, and named entities from a piece of text.
Before we start, make sure the SpaCy wrapper is installed.
```bash
pip install forte.spacy
```
Let's start by writing a simple processor that analyze POS tags to tokens using the good old NLTK library.
```python
import nltk
from forte.processors.base import PackProcessor
from forte.data.data_pack import DataPack
from ft.onto.base_ontology import Token
class NLTKPOSTagger(PackProcessor):
r"""A wrapper of NLTK pos tagger."""
def initialize(self, resources, configs):
super().initialize(resources, configs)
# download the NLTK average perceptron tagger
nltk.download("averaged_perceptron_tagger")
def _process(self, input_pack: DataPack):
# get a list of token data entries from `input_pack`
# using `DataPack.get()`` method
token_texts = [token.text for token in input_pack.get(Token)]
# use nltk pos tagging module to tag token texts
taggings = nltk.pos_tag(token_texts)
# assign nltk taggings to token attributes
for token, tag in zip(token_entries, taggings):
token.pos = tag[1]
```
If we break it down, we will notice there are two main functions.
In the `initialize` function, we download and prepare the model. And then in the `_process`
function, we actually process the `DataPack` object, take the some tokens from it, and
use the NLTK tagger to create POS tags. The results are stored as the `pos` attribute of
the tokens.
Before we go into the details of the implementation, let's try it in
a full pipeline.
```python
from forte import Pipeline
from forte.data.readers import TerminalReader
from fortex.spacy import SpacyProcessor
pipeline: Pipeline = Pipeline[DataPack]()
pipeline.set_reader(TerminalReader())
pipeline.add(SpacyProcessor(), {"processors": ["sentence", "tokenize"]})
pipeline.add(NLTKPOSTagger())
```
Here we have successfully created a pipeline with a few components:
* a `TerminalReader` that reads data from terminal
* a `SpacyProcessor` that calls SpaCy to split the sentences and create tokenization
* and finally the brand new `NLTKPOSTagger` we just implemented,
Let's see it run in action!
```python
for pack in pipeline.initialize().process_dataset():
for sentence in pack.get("ft.onto.base_ontology.Sentence"):
print("The sentence is: ", sentence.text)
print("The POS tags of the tokens are:")
for token in pack.get(Token, sentence):
print(f" {token.text}({token.pos})", end = " ")
print()
```
We have successfully created a simple pipeline. In the nutshell, the `DataPack`s are
the standard packages "flowing" on the pipeline. They are created by the reader, and
then pass along the pipeline.
Each processor, such as our `NLTKPOSTagger`,
interfaces directly with `DataPack`s and do not need to worry about the
other part of the pipeline, making the engineering process more modular. In this example
pipeline, `SpacyProcessor` creates the `Sentence` and `Token`, and then we implemented
the `NLTKPOSTagger` to add Part-of-Speech tags to the tokens.
To learn more about the details, check out of [documentation](https://asyml-forte.readthedocs.io/)!
The classes used in this guide can also be found in this repository or
[the Forte Wrappers repository](https://github.com/asyml/forte-wrappers/tree/main/src/spacy)
## And There's More
The data-centric abstraction of Forte opens the gate to many other opportunities.
Not only does Forte allow engineers to develop reusable components easily, it further provides a simple way to develop composable ML modules. For example, Forte allows us to:
* create composable ML solutions with reusable models and processing logic
* easily interface with a great collection of [3rd party toolkits](https://github.com/asyml/forte-wrappers) built by the community
* build plug-and-play [data augmentation tools](https://asyml-forte.readthedocs.io/en/latest/code/data_aug.html)
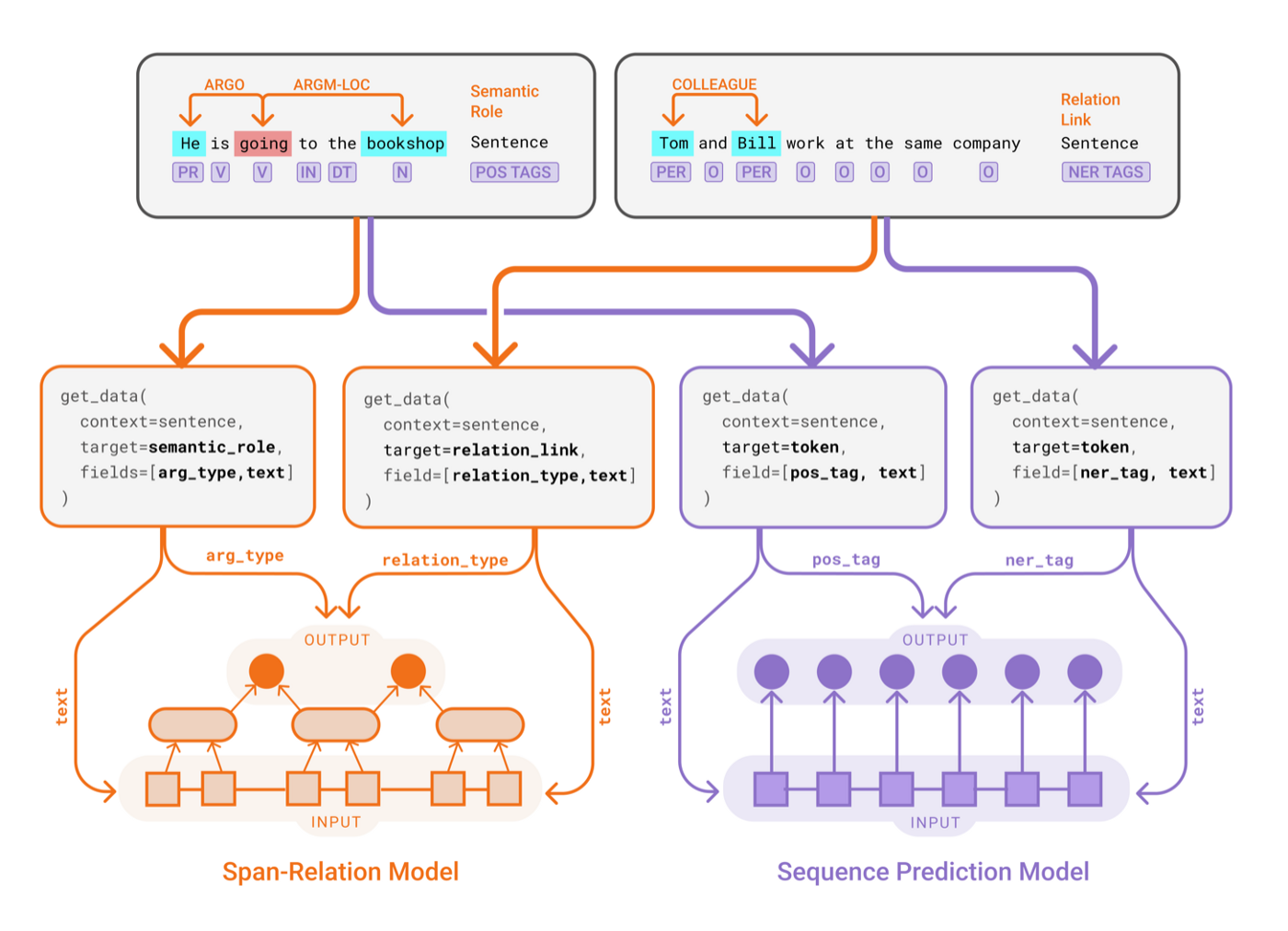
To learn more about these, you can visit:
* [Examples](https://github.com/asyml/forte/tree/master/examples)
* [Documentation](https://asyml-forte.readthedocs.io/)
* Currently we are working on some interesting [tutorials](https://asyml-forte.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index_toc.html), stay tuned for a full set of documentation on how to do NLP with Forte!
## Contributing
Forte was originally developed in CMU and is actively contributed by [Petuum](https://petuum.com/) in collaboration with other institutes. This project is part of the [CASL Open Source](http://casl-project.ai/) family.
If you are interested in making enhancement to Forte, please first go over our [Code of Conduct](https://github.com/asyml/forte/blob/master/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md) and [Contribution Guideline](https://github.com/asyml/forte/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md)
## About
### Supported By
<p align="center">
<img src="https://asyml.io/assets/institutions/cmu.png", width="200" align="top">
<img src="https://www.ucsd.edu/_resources/img/logo_UCSD.png" width="200" align="top">
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/asyml/forte/master/docs/_static/img/Petuum.png" width="200" align="top">
</p>

### License
[Apache License 2.0](https://github.com/asyml/forte/blob/master/LICENSE)




