# Emblaze - Interactive Embedding Comparison
Emblaze is a Jupyter notebook widget for **visually comparing embeddings** using animated scatter plots. It bundles an easy-to-use Python API for performing dimensionality reduction on multiple sets of embedding data (including aligning the results for easier comparison), and a full-featured interactive platform for probing and comparing embeddings that runs within a Jupyter notebook cell. [Read the documentation >](https://dig.cmu.edu/emblaze/emblaze)
## Installation
**Compatibility Note:** Note that this widget has been tested using Python >= 3.7. If you are using JupyterLab, please make sure you are running version 3.0 or higher. The widget currently does not support displaying in the VS Code interactive notebook environment.
Install Emblaze using `pip`:
```bash
pip install emblaze
```
The widget should work out of the box when you run `jupyter lab` (see example code below).
_Jupyter Notebook note:_ If you are using Jupyter Notebook 5.2 or earlier, you may also need to enable
the nbextension:
```bash
jupyter nbextension enable --py --sys-prefix emblaze
```
## Examples
Please see `examples/example.ipynb` to try using the Emblaze widget on the Boston housing prices or MNIST (TensorFlow import required) datasets.
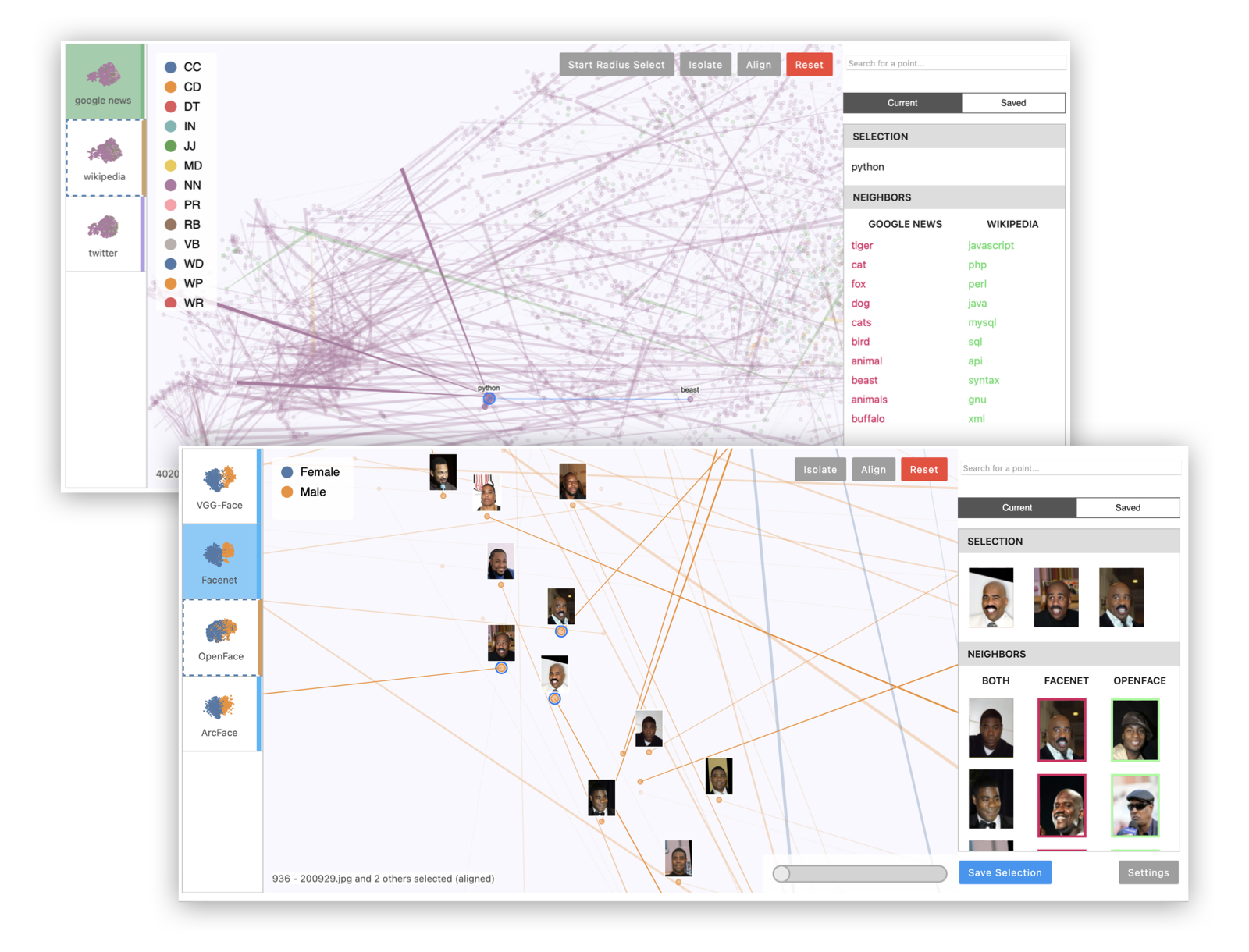
**Example 1: Multiple projections of the same embedding dataset.** This can reveal areas of variation in the dimensionality reduction process, since tSNE and UMAP are randomized algorithms.
```python
import emblaze
from emblaze.utils import Field, ProjectionTechnique
# X is an n x k array, Y is a length-n array
X, Y = ...
# Represent the high-dimensional embedding
emb = emblaze.Embedding({Field.POSITION: X, Field.COLOR: Y})
# Compute nearest neighbors in the high-D space (for display)
emb.compute_neighbors(metric='cosine')
# Generate UMAP 2D representations - you can pass UMAP parameters to project()
variants = emblaze.EmbeddingSet([
emb.project(method=ProjectionTechnique.UMAP) for _ in range(10)
])
# Compute neighbors again (to indicate that we want to compare projections)
variants.compute_neighbors(metric='euclidean')
w = emblaze.Viewer(embeddings=variants)
w
```
**Example 2: Multiple embeddings of the same data from different models.** This is useful to see how different models embed data differently.
```python
# Xs is a list of n x k arrays corresponding to different embedding spaces
Xs = ...
# Y is a length-n array of labels for color-coding
Y = ...
# List of strings representing the name of each embedding space (e.g.
# "Google News", "Wikipedia", "Twitter"). Omit to use generic names
embedding_names = [...]
# Make high-dimensional embedding objects
embeddings = emblaze.EmbeddingSet([
emblaze.Embedding({Field.POSITION: X, Field.COLOR: Y}, label=emb_name)
for X, emb_name in zip(Xs, embedding_names)
])
embeddings.compute_neighbors(metric='cosine')
# Make aligned UMAP
reduced = embeddings.project(method=ProjectionTechnique.ALIGNED_UMAP)
w = emblaze.Viewer(embeddings=reduced)
w
```
**Example 3: Visualizing image data with image thumbnails.** The viewer will display image previews for each point as well as its nearest neighbors. (For text data, you can use `TextThumbnails` to show small pieces of text next to the points.)
```python
# images is an n x 100 x 100 x 3 numpy array of 100x100 RGB images (values from 0-255)
images = ...
thumbnails = emblaze.ImageThumbnails(images)
w = emblaze.Viewer(embeddings=embeddings, thumbnails=thumbnails)
w
```
You can also visualize embeddings with multimodal labels (i.e. where some points have text labels and others have image labels) by initializing an `emblaze.CombinedThumbnails` instance with a list of other `Thumbnails` objects to combine.
See the [documentation](https://dig.cmu.edu/emblaze/emblaze) for more details on defining and configuring comparisons with Emblaze.
---
## Development Installation
Clone repository, then install dependencies:
```bash
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
Install the python package. This will also build the JS packages.
```bash
pip install -e .
```
Run the following commands if you use **Jupyter Lab**:
```
jupyter labextension install @jupyter-widgets/jupyterlab-manager --no-build
jupyter labextension install .
```
Run the following commands if you use **Jupyter Notebook**:
```
jupyter nbextension install --sys-prefix --symlink --overwrite --py emblaze
jupyter nbextension enable --sys-prefix --py emblaze
```
Note that the `--symlink` flag doesn't work on Windows, so you will here have to run
the `install` command every time that you rebuild your extension. For certain installations
you might also need another flag instead of `--sys-prefix`, but we won't cover the meaning
of those flags here.
### How to see your changes
Open JupyterLab in watch mode with `jupyter lab --watch`. Then, in a separate terminal, watch the source directory for changes with `npm run watch`. After a change to the JavaScript code, you will wait for the build to finish, then refresh your browser. After changing in Python code, you will need to restart the notebook kernel to see your changes take effect.
### Standalone App Development
To develop using the standalone app, run `npm run watch:standalone` in a separate terminal from the Flask server to continuously build the frontend. You will need to reload the page to see your changes.
The standalone application serves datasets stored at the data path that is printed when the Flask server starts (should be something like `.../lib/python3.9/site-packages/emblaze/data` for the pip-installed version, or `.../emblaze/emblaze/data` for a local repository). You can add your own datasets by building an `EmbeddingSet` and (optionally) a `Thumbnails` object, then saving the results to files in the data directory:
```python
import os, json
dataset_name = "my-dataset"
data_dir = ... # data directory printed by flask server
embeddings = ... # EmbeddingSet object
thumbnails = ... # (Text|Image)Thumbnails object
os.mkdir(os.path.join(data_dir, dataset_name))
with open(os.path.join(data_dir, dataset_name, "data.json"), "w") as file:
json.dump(embeddings.to_json(), file)
with open(os.path.join(data_dir, dataset_name, "thumbnails.json"), "w") as file:
json.dump(thumbnails.to_json(), file)
```
### Building Documentation
Install pdoc3: `pip install pdoc3`
Build documentation:
```bash
pdoc --html --force --output-dir docs --template-dir docs/templates emblaze
```
### Deployment
First clean all npm build intermediates:
```
npm run clean
```
Bump the widget version in `emblaze/_version.py`, `emblaze/_frontend.py`, and `package.json` if applicable. Then build the notebook widgets and standalone app:
```
npm run build:all
```
Run the packaging script to generate the wheel for distribution:
```
python -m build
```
Upload to PyPI (replace `<VERSION>` with the version number):
```
twine upload dist/emblaze-<VERSION>*
```
### Development Notes
- Svelte transitions don't seem to work well as they force an expensive re-layout operation. Avoid using them during interactions.




