> Consider the project as a proof of concept! Definitely not production ready!
# Dynafile
Embedded pure Python NoSQL database following DynamoDB concepts.
```bash
pip install dynafile
# with string filter support using filtration
pip install "dynafile[filter]"
# bloody edge
pip install git+https://github.com/eruvanos/dynafile.git
pip install filtration
```
## Overview
Dynafile stores items within partitions, which are stored as separate files. Each partition contains a SortedDict
from `sortedcontainers` which are sorted by the sort key attribute.
Dynafile does not implement the interface or functionality of DynamoDB, but provides familiar API patterns.
Differences:
- Embedded, file based
- No pagination
## Features
- persistence
- put item
- get item
- delete item
- scan - without parameters
- query - starts_with
- query - index direction
- query - filter
- scan - filter
- batch writer
- atomic file write
- event stream hooks (put, delete)
- TTL
## Roadmap
- GSI - global secondary index
- update item
- batch get
- thread safeness
- LSI - local secondary index
- split partitions
- parallel scans - pre defined scan segments
- transactions
- optimise disc load time (cache partitions in memory, invalidate on file change)
- conditional put item
- improve file consistency (options: acidfile)
## API
```python
from dynafile import *
# init DB interface
db = Dynafile(path=".", pk_attribute="PK", sk_attribute="SK")
# put items
db.put_item(item={"PK": "user#1", "SK": "user#1", "name": "Bob"})
db.put_item(item={"PK": "user#1", "SK": "role#1", "TYPE": "sender"})
db.put_item(item={"PK": "user#2", "SK": "user#2", "name": "Alice"})
# more performant batch operation
with db.batch_writer() as writer:
db.put_item(item={"PK": "user#3", "SK": "user#3", "name": "Steve"})
db.delete_item(key={"PK": "user#3", "SK": "user#3"})
# retrieve items
item = db.get_item(key={
"PK": "user#1",
"SK": "user#1"
})
# query item collection by pk
items = list(db.query(pk="user#1"))
# scan full table
items = list(db.scan())
# add event stream listener to retrieve item modification
def print_listener(event: Event):
print(event.action)
print(event.old)
print(event.new)
db.add_stream_listener(print_listener)
```
### Filter
`query` and `scan` support filter, you can provide callables as filter like lambda expressions.
Another option are [filtration](https://pypi.org/project/filtration/) expressions.
* Equal ("==")
* Not equal ("!=")
* Less than ("<")
* Less than or equal ("<=")
* Greater than (">")
* Greater than or equal (">=")
* Contains ("in")
* RHS must be a list or a Subnet
* Regular expression ("=~")
* RHS must be a regex token
Examples:
* `SK =~ /^a/` - SK starts with a
* `SK == 1` - SK is equal 1
* `SK == 1` - SK is equal 1
* `nested.a == 1` - accesses nested structure `item.nested.a`
### TTL - Time To Live
TTL provides the option to expire items on read time (get, query, scan).
```python
import time
from dynafile import *
db = Dynafile(path=".", pk_attribute="PK", sk_attribute="SK", ttl_attribute="ttl")
item = {"PK": "1", "SK": "2", "ttl": time.time() - 1000} # expired ttl
db.put_item(item=item)
list(db.scan()) # -> []
```
## Architecture
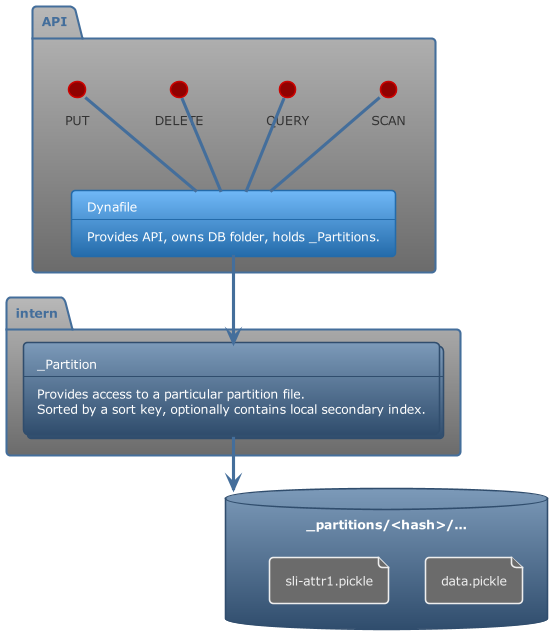
### File Structure
```text
--- ROOT ---
./db/
--- MAIN DB ---
|- meta.json - meta information
|- _partitions/
|- <hash>/
|- data.pickle - Contains partition data by sort key (SortedDict)
|- lsi-attr1.pickle - Contains partition data by lsi attr (SortedDict)
--- GSI ---
|- _gsi-<gsi-name>/
|- _partitions/
|- <hash>/
|- data.pickle - Contains partition data by sort key (SortedDict)
```




