# CoSaMP
CoSaMP algorithm in Python. <br/>
## Installation
How to install:
```
pip install cosamp
```
or
```
pip3 install cosamp
```
Dependencies: **numpy**.
## Usage example
```
@Input: Phi - Sampling matrix
u - Noisy sample vector
s - Sparsity vector
@Return: A s-sparse approximation "a" of the target signal
```
Using CoSaMP algorithm to reconstruct a high-frequency signal from sparse measurements:
```python
import numpy as np
import scipy.linalg
import scipy.signal
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from cosamp import cosamp
n = 100 # number of measurements
t = np.linspace(0.0, 1.0, num=n)
x = np.sin(91*2*np.pi*t) + np.sin(412*2*np.pi*t) # original signal (to be reconstructed)
# randomly sample signal
p = 103 # random sampling (Note that this is one eighth of the Shannon–Nyquist rate!)
aquis = np.round((n-1) * np.random.rand(p)).astype(int)
y = x[aquis] # our compressed measurement from the random sampling
# Here {y} = [C]{x} = [C][Phi]{s}, where Phi is the inverse discrete cosine transform
Phi = scipy.fft.dct(np.eye(n), axis=0, norm='ortho')
CPhi = Phi[aquis,:]
# l1 minimization (through linear programming)
s = cosamp.cosamp(CPhi, y, 10) # obtain the sparse vector through CoSaMP algorithm
xrec = scipy.fft.idct(s, axis=0, norm='ortho') # Reconstructed signal
figw, figh = 7.0, 5.0 # figure width and height
plt.figure(figsize=(figw, figh))
plt.plot(t, s)
plt.title('Sparse vector $s$')
plt.show()
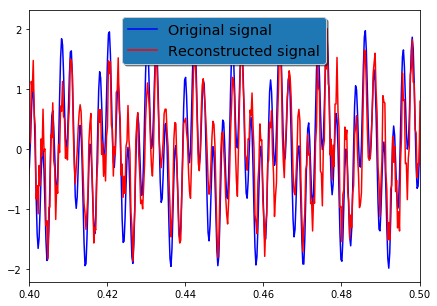
# Visualize the compressed-sensing reconstruction signal
figw, figh = 7.0, 5.0 # figure width and height
plt.figure(figsize=(figw, figh))
plt.plot(t, x, 'b', label='Original signal')
plt.plot(t, xrec, 'r', label='Reconstructed signal')
plt.xlim(0.4, 0.5)
legend = plt.legend(loc='upper center', shadow=True, fontsize='x-large')
# Put a nicer background color on the legend.
legend.get_frame().set_facecolor('C0')
plt.show()
```

## Other info
MATLAB versions of the algorithm are readly available (see [here](https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/32402-cosamp-and-omp-for-sparse-recovery) for instance). This Python method is based on the MATLAB routine written by Prof. Bob L. Sturm.
The original Needell and Tropp's 2008 paper can be found [here](http://users.cms.caltech.edu/~jtropp/papers/NT08-CoSaMP-Iterative-preprint.pdf).




