# clock
Simple command-line time tracker based on a simple text file format.
# Introduction
This simple utility uses a text file to store tasks with date/time information. Each time you start working on a task, a new line is created on the file with the current time and a description of the task you are starting to work on.
At the end of the day, or anytime, you can then generate reports and statistics based on the file.
## File structure
The file structure is very simple and can be edited using the script or directly with your favorite text editor.
Here is an example file:
```
[2022-01-01]
10:00 Starting project X +projectX
11:23 Starting documentation of project X +projectX +doc
12:00 [Stop]
[2022-01-02]
08:05 Starting workday, checking emails +office +emails
09:00 Back on documentation +projectX +doc
10:00 [Stop]
```
## Tags and ids
An entry in this file can be associated with tags if you start the tag with a `+` (`+tag`) or ID if you start with a `.` (`.456`).
Tags allow for powerful filtering and reporting. They are ordered, meaning that `+project +doc` is different from `+doc +project` (see reports and filters below).
IDs allow to track time of tasks from an external tool, such as Jira. Entries with an ID are automatically assigned a default tag (`+jira`).
## Special tasks
The `[Stop]` task is used to stop the last task. It is not required if you switch tasks without taking a break.
# Installation
The program is available as a python packge through Pypi, so you can download it using pip:
```
python -m pip install clock-tracking
```
## Creating an alias
You can create a shortcut (alias) to make the package easier to be called from the command line. Follow the instructions below depending on your operating system.
### Windows PowerShell
On Windows, you can use the script with PowerShell. To create an alias permenantly, open your `profile.ps1` file (see [Windows PowerShell Profiles](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/microsoft.powershell.core/about/about_profiles?view=powershell-7.2)) and add these lines:
```powershell
function Invoke-Clock { python -m clock_tracking $args }
New-Alias -Name clock -Value Invoke-Clock
```
### MacOS / Unix
Open your bash profile (see [Bash Profiles](https://www.gnu.org/software/bash/manual/html_node/Bash-Startup-Files.html)) and add these lines:
```bash
alias clock="python -m clock_tracking"
```
# Usage
## Tracking tasks
Use the `clock_tracking` python package to run the program, i.e. `python -m clock_tracking` or directly the command alias (see above). In this documentation, we'll use the alias `clock` to call the `python -m clock_tracking` package.
You can add a new entry by adding the entry definition after the package name:
```
$ clock Definition of the prototype +myapp +proto
Added: 08:10 Definition of the prototype +myapp +proto
Duration Date Start Stop Tags Name IDs
00:00 2022-01-01 08:10 08:10 +myapp,+proto Definition of the prototype
```
To switch to a new task, just use the same command:
```
$ clock Switching to new task
Added: 09:02 Switching to a new task
Duration Date Start Stop Tags Name IDs
00:00 2022-01-01 08:10 08:10 Switching to a new task
```
This will automatically stop the last task and start a new one. When you have finished working, use the `stop` command:
```
$ clock stop
Added: 10:00 [Stop]
```
## Reports
You can show reports/statistics with the `show` command:
```
$ clock show
```
All tasks are ordered by first tag by default. Several filters are available, see `./clock --help` for the full documentation.
To show all the tasks with their details:
```
$ clock show --details
```
To filter by a tag:
```
$ clock show +tag
```
To filter by an ID:
```
$ clock show .345
```
## Examples
Report by tags / projects:

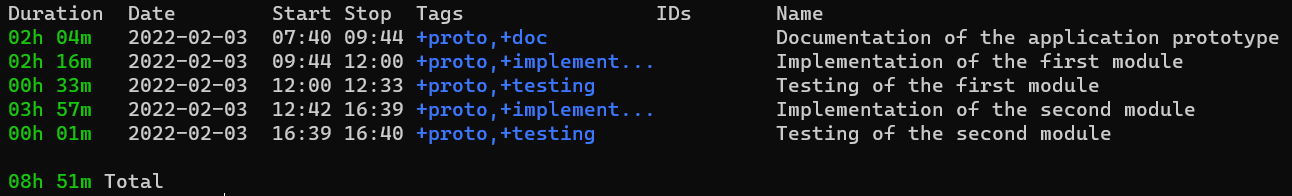
Show today's tasks details:
## Documentation
```
usage: __main__.py [-h] [-f FILE] [--target HH:MM] [--target-per-day HH:MM] [-a HH:MM] [-t] [-w] [-s YYYY-mm-dd] [-e YYYY-mm-dd] [-l n] [-d]
[--categories] [--timeline]
command
Helps managing time tracking from the command-line
positional arguments:
command Command (add, edit, show). add: add a new entry. edit: edit current entry's description. show: show reports and statistics.
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
settings:
-f FILE, --file FILE Speficy the file to store time entries. Default is ~/clock.txt
--target HH:MM <show> Sets expected target time (format HH:MM) and computes the difference with actual times in the reports
--target-per-day HH:MM
<show> Sets expected target time per day (format HH:MM) and computes the difference with actual times in the reports
add:
-a HH:MM, --at HH:MM <add> Specify a time (format HH:MM) of a new entry
filters:
-t, --today <show> Show only entries from today
-w, --week <show> Show only entries from the current week
-s YYYY-mm-dd, --from YYYY-mm-dd
<show> Include entries with start date later or equal to given date (format YYYY-mm-dd)
-e YYYY-mm-dd, --to YYYY-mm-dd
<show> Include entries with start date earlier or equal to given date (format YYYY-mm-dd)
-l n, --last n <show> Show only the last n entries
reports:
-d, --details <show> Shows detailed report
--categories <show> Shows categories report (default)
--timeline <show> Shows issues on a timeline (only when --today is specified)
```




