[](https://badge.fury.io/py/bwsample)
[](https://img.shields.io/pypi/dm/bwsample)
[](https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03324)
[](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/335090754)
[](https://gitter.im/satzbeleg/community?utm_source=badge&utm_medium=badge&utm_campaign=pr-badge&utm_content=badge)
[](https://snyk.io/advisor/python/bwsample)
# bwsample: Sampling and Evaluation of Best-Worst Scaling sets
Sampling algorithm for best-worst scaling (BWS) sets, extracting pairs from evaluated BWS sets, count in dictionary of keys sparse matrix, and compute scores based on it.
The package `bwsample` addresses three areas:
* [Sampling](#sampling)
* [Counting](#counting)
* [Ranking](#ranking)
## Installation
The `bwsample` [git repo](http://github.com/satzbeleg/bwsample) is available as [PyPi package](https://pypi.org/project/bwsample)
```sh
pip install "bwsample>=0.7.0"
```
## Overview
The `bwsample` can be deployed at different stages to prepare BWS example sets and post-process evaluated BWS sets.
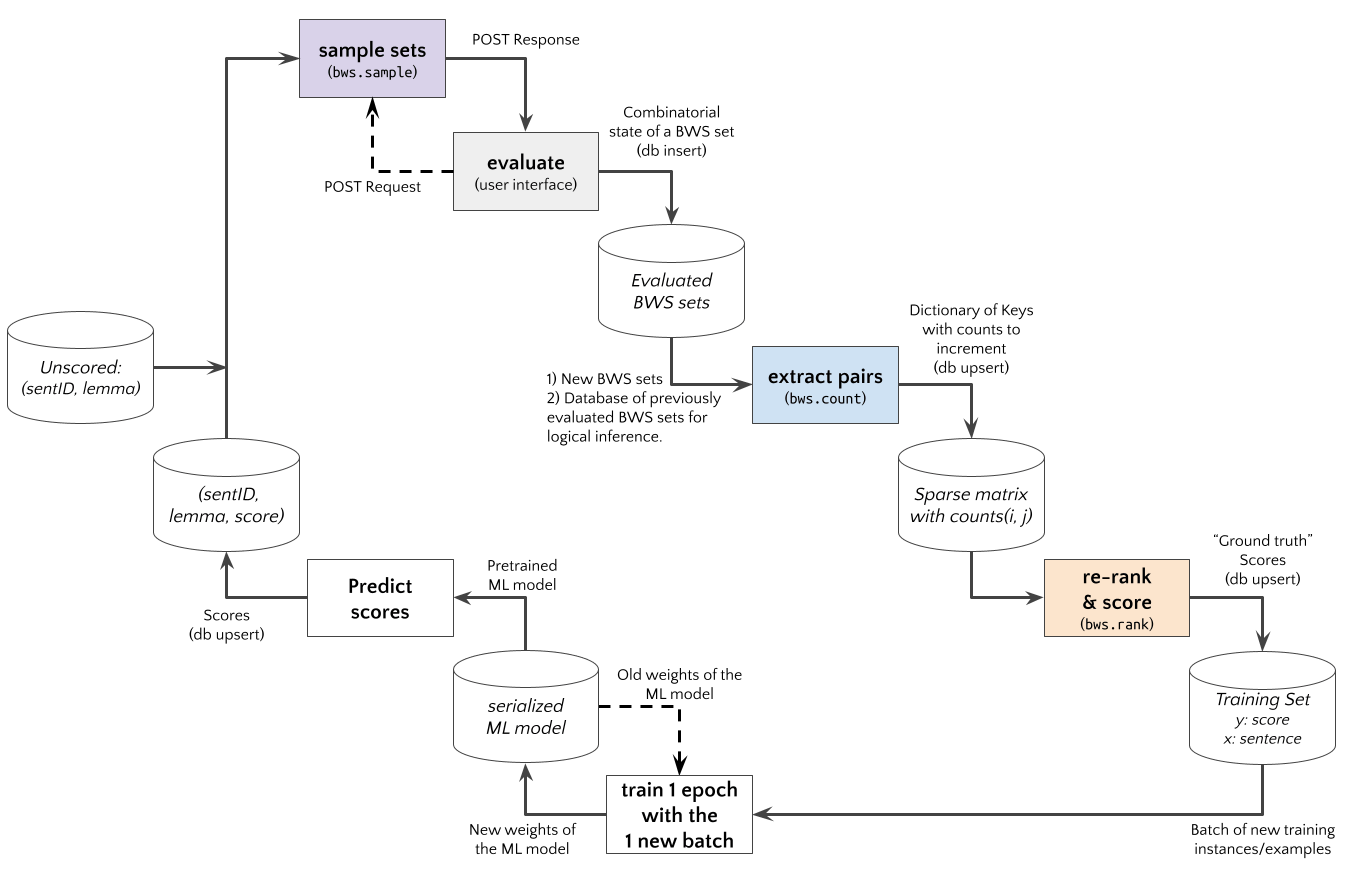
An *Active Learning* experiment using an Web App with BWS user interface to judge sentence examples is shown in the diagram below. The `bwsample` would be implemented in a (python based) REST API. The App requests new BWS example sets, and `bwsample.sample` generates these. After the App posts the evaluation results to the API, `bwsample.count` extract new pairwise data from evaluated BWS sets. The pairwise comparision matrix can be used by `bwsample.rank` to compute scores for a new updated training set.
## Sampling
**Input Data:**
The input data `examples` for `bwsample.sample` should be a `List[anything]`.
For example, `List[Dict[ID,DATA]]` with identifiers using the key `"id"` and the associated data using the key `"data"`, e.g.
```python
examples = [
{"id": "id1", "data": "data..."},
{"id": "id2", "data": ["other", "data"]},
{"id": "id3", "data": {"key", "value"}},
{"id": "id4", "data": "lorem"},
{"id": "id5", "data": "ipsum"},
{"id": "id6", "data": "blind"},
{"id": "id7", "data": "text"}
]
```
**Call the function:**
The number of items per BWS set `n_items` (`M`) must be specified, e.g. `n_items=4` if your App displays four items.
The `'overlap'` algorithm assigns every `i*(M-1)+1`-th example to two consecutive BWS sets, so that `1/(M-1)` of examples are evaluated two times.
The `'twice'` algorithm connects the remaining `(M-2)/(M-1)` non-overlapping from `'overlapping'` so that all examples occur twice.
The total number of sampled BWS sets might differ accordingly.
```python
import bwsample as bws
samples = bws.sample(examples, n_items=4, method='overlap')
```
**Output Data:**
The output has the following structure
```
[
[{'id': 'id1', 'data': 'data...'}, {'id': 'id2', 'data': ['other', 'data']}, {'id': 'id3', 'data': {'key', 'value'}}, {'id': 'id4', 'data': 'lorem'}],
[{'id': 'id1', 'data': 'data...'}, {'id': 'id4', 'data': 'lorem'}, {'id': 'id5', 'data': 'ipsum'}, {'id': 'id6', 'data': 'blind'}]
]
```
**Warning**: `len(examples)` must be a multiple of `(n_items - 1)`
**References:**
- Section 5 (page 4) in: Hamster, U. A. (2021, March 9). Extracting Pairwise Comparisons Data from Best-Worst Scaling Surveys by Logical Inference. [https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/qkxej](https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/qkxej)
## Counting
**Input Data:**
The input data`evaluations` for `bwsample.count` should structured as `List[Tuple[List[ItemState], List[ItemID]]]`.
The labelling/annotation application should produce a list of item states `List[ItemState]` with the states `BEST:1`, `WORST:2` and `NOT:0` for each item.
And the corresponding list of IDs `List[ItemID]` for each item or resp. example.
```python
evaluations = (
([0, 0, 2, 1], ['id1', 'id2', 'id3', 'id4']),
([0, 1, 0, 2], ['id4', 'id5', 'id6', 'id7']),
([1, 2, 0, 0], ['id7', 'id8', 'id9', 'id1'])
)
```
**Call the function:**
```python
import bwsample as bws
agg_dok, direct_dok, direct_detail, logical_dok, logical_detail = bws.count(evaluations)
```
**Output Data:**
The function `bwsample.count` outputs Dictionary of Keys (DOK) with the data structure `Dict[Tuple[ItemID, ItemID], int]`, e.g. `agg_dok`, `direct_dok`, `direct_detail["bw"]`, etc., what contain variants which pairs where counted:
- `agg_dok`
- `direct_dok`
- `direct_detail["bw"]` -- `BEST>WORST`
- `direct_detail["bn"]` -- `BEST>NOT`
- `direct_detail["nw"]` -- `NOT>WORST`
- `logical_dok`
- `logical_detail["nn"]` -- `D>E>F vs X>E>Z`
- `logical_detail["nb"]` -- `D>E>F vs E>Y>Z`
- `logical_detail["nw"]` -- `D>E>F vs X>Y>E`
- `logical_detail["bn"]` -- `D>E>F vs X>D>Z`
- `logical_detail["bw"]` -- `D>E>F vs X>Y>D`
- `logical_detail["wn"]` -- `D>E>F vs X>F>Z`
- `logical_detail["wb"]` -- `D>E>F vs F>Y>Z`
**Limit the Database Size:**
Logical Inference has quadratic complexity, and it might be beneficial to limit the database what can be done by the `logical_database` parameter.
```python
import bwsample as bws
agg_dok, direct_dok, direct_detail, logical_dok, logical_detail = bws.count(
evaluations, logical_database=evaluations[:1])
```
**Update Frequencies:**
The function `bwsample.count` is an update function, i.e. you can provide previous count or resp. frequency data (e.g. `logical_dok`) or start from scratch (e.g. `agg_dok=None`).
```python
import bwsample as bws
evaluations = [...]
direct_dok = {...}
direct_detail = {...}
logical_dok = {...}
logical_detail = {...}
database = [...]
agg_dok, direct_dok, direct_detail, logical_dok, logical_detail = bws.count(
evaluations, direct_dok=direct_dok, direct_detail=direct_detail,
logical_dok=logical_dok, logical_detail=logical_detail, logical_database=database)
```
**References:**
- Section 3-4 in: Hamster, U. A. (2021, March 9). Extracting Pairwise Comparisons Data from Best-Worst Scaling Surveys by Logical Inference. [https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/qkxej](https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/qkxej)
## Ranking
**Input Data:**
The input data is a Dictionary of Keys (DoK) object produced by `bwsample.count`.
**Call the function:**
The function `bwsample.rank` computes a python index variable with a proposed ordering (`ranked`), and ordered list of example IDs (`ordids`), scores (`scores`) and further information depending on the selected `method`.
```python
import bwsample as bws
ranked, ordids, metrics, scores, info = bws.rank(dok, method='ratio', adjust='quantile')
```
**Available methods:**
Computed from extracted pairs:
- `'ratio'` -- Simple ratios for each pair, and sum ratios for each item.
- `'approx'` -- Chi-Squared based p-value (Hoaglin Approximation) for each pair, and sum 1-pval for each item (Beh et al, 2018)
- `'btl'` -- Bradley-Terry-Luce (BTL) model estimated with MM algorithm (Hunter, 2004).
- `'eigen'` -- Eigenvectors of the reciprocal pairwise comparison matrix (Saaty, 2003).
- `'trans'` -- Estimate transition probability of the next item to be better.
The implementations `ratio`, `pvalue`, `'btl'`, `'eigen'`, and `'trans'` are fully based on sparse matrix operations and `scipy.sparse` algorithms, and avoid accidental conversions to dense matrices.
**References:**
- Hoaglin Approximation for p-values: Beh, E., 2018. Exploring How to Simply Approximate the P-value of a Chi-squared Statistic. AJS 47, 63–75. [https://doi.org/10.17713/ajs.v47i3.757](https://doi.org/10.17713/ajs.v47i3.757)
- Eigenvector solution in: Saaty, T. L. (2003). Decision-making with the AHP: Why is the principal eigenvector nec- essary. European Journal of Operational Research, 145(1), 85–91. [https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(02)00227-8](https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(02)00227-8)
- Estimating the BTL model in: Hunter, D. R. (2004). MM algorithms for generalized Bradley-Terry models. The Annals of Statistics, 32(1), 384–406. [https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1079120141](https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1079120141)
- MaxDiff score in: Orme, B. (2009). MaxDiff Analysis: Simple Counting, Individual-Level Logit, and HB. [https://sawtoothsoftware.com/uploads/sawtoothsoftware/originals/f89a6537-1cae-4fb5-afad-9d325c2a3143.pdf](https://sawtoothsoftware.com/uploads/sawtoothsoftware/originals/f89a6537-1cae-4fb5-afad-9d325c2a3143.pdf)
- Hamster, U. A. (2021, April 1). Pairwise comparison based ranking and scoring algorithms. [https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/ev7fw](https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/ev7fw)
## Appendix
### Install a virtual environment
In order to run the Jupyter notebooks or want to work on this project (e.g. unit tests, syntax checks) you should install a Python virtual environment.
```sh
python3.7 -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt --no-cache-dir
pip install -r requirements-dev.txt --no-cache-dir
pip install -r requirements-demo.txt --no-cache-dir
```
(If your git repo is stored in a folder with whitespaces, then don't use the subfolder `.venv`. Use an absolute path without whitespaces.)
### Python commands
* Jupyter for the examples: `jupyter lab`
* Check syntax: `flake8 --ignore=F401 --exclude=$(grep -v '^#' .gitignore | xargs | sed -e 's/ /,/g')`
* Run Unit Tests: `pytest`
Publish
```sh
# pandoc README.md --from markdown --to rst -s -o README.rst
python setup.py sdist
twine check dist/*
twine upload -r pypi dist/*
```
### Clean up
```sh
find . -type f -name "*.pyc" | xargs rm
find . -type d -name "__pycache__" | xargs rm -r
rm -r .pytest_cache
rm -r .venv
```
### Support
Please [open an issue](https://github.com/satzbeleg/bwsample/issues/new) for support.
### Contributing
Please contribute using [Github Flow](https://guides.github.com/introduction/flow/). Create a branch, add commits, and [open a pull request](https://github.com/satzbeleg/bwsample/compare/).
### Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) - [433249742](https://gepris.dfg.de/gepris/projekt/433249742). Project duration: 2020-2023.
### Citation
Please cite the peer-reviewed JOSS paper [](https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03324) when using this software for any purpose.




