# bioLEC - _Landscape Elevational Connectivity Package_
[](https://hub.docker.com/r/geodels/biolec)
[](https://pypi.org/project/bioLEC/) [](https://biolec.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
**bioLEC** documentation is found at [**biolec.readthedocs.io**](https://biolec.readthedocs.io/)
**bioLEC** is a parallel python package built to calculate the *Landscape elevational connectivity* (**LEC**).
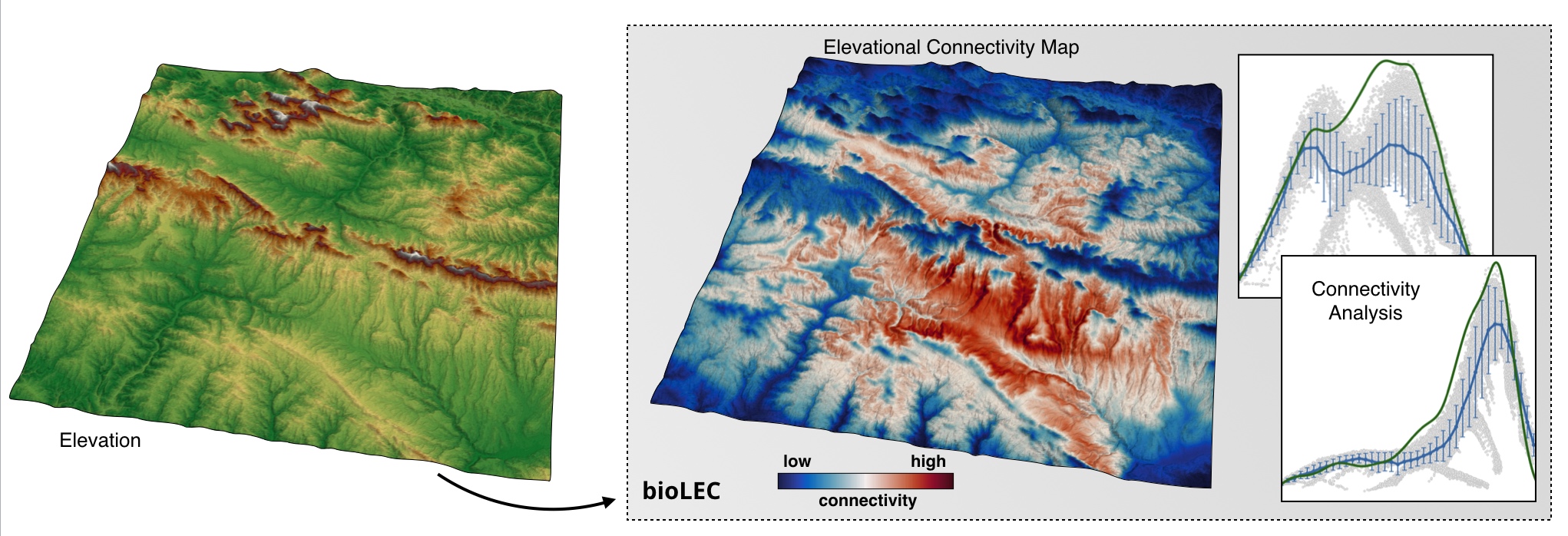
**LEC** quantifies the closeness of a site to all others with **similar elevation**. It measures how easily a **species living in a given patch can spread and colonise other patches**. It is assumed to be **elevation-dependent** and the metric depends on how often a species adapted to a given elevation *needs to travel outside its optimal elevation range* when moving from its patch to any other in the landscape [Bertuzzo et al., 2016].
## Installation
### Dependencies
You will need **Python 2.7 or 3.5+**.
Also, the following packages are required:
- [`numpy`](http://numpy.org)
- [`scipy`](https://scipy.org)
- [`pandas`](https://pandas.pydata.org/)
- [`mpi4py`](https://pypi.org/project/mpi4py/)
- [`scikit-image`](https://scikit-image.org/)
- [`rasterio`](https://pypi.org/project/rasterio/)
### Installing using pip
You can install `bioLEC` using the
[`pip package manager`](https://pypi.org/project/pip/) with either version of Python:
```bash
python2 -m pip install bioLEC
python3 -m pip install bioLEC
```
### Installing using Docker
A more straightforward installation which does not depend on specific compilers relies on the [docker](http://www.docker.com) virtualisation system.
To install the docker image and test it is working:
```bash
docker pull geodels/biolec:latest
docker run --rm geodels/biolec:latest help
```
To build the dockerfile locally, we provide a script. First ensure you have checked out the source code from github and then run the script in the Docker directory. If you modify the dockerfile and want to push the image to make it publicly available, it will need to be retagged to upload somewhere other than the GEodels repository.
```bash
git checkout https://github.com/Geodels/bioLEC.git
cd bioLEC
source Docker/build-dockerfile.sh
```
## Usage
### Binder & docker container
Launch the demonstration at [mybinder.org](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/Geodels/bioLEC/binder?filepath=Notebooks%2F0-StartHere.ipynb)
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/Geodels/bioLEC/binder?filepath=Notebooks%2F0-StartHere.ipynb)

> _Notebooks environment_ will not be the best option for _large landscape models_ and we will recommend the use of the python script: `runLEC.py` in HPC environment. the code will need to be
```bash
mpirun -np 400 python runLEC.py
```
Or using the Docker container available through Kitematic **geodels/biolec**.
[](https://hub.docker.com/r/geodels/biolec)

## Collaborations
### How to contribute?
**We welcome all kinds of contributions!** Please get in touch if you would like to help out.
> Everything from **code** to **notebooks** to **examples** and **documentation** are all equally valuable so please don't feel you can't contribute.
To contribute please **fork the project make your changes and submit a pull request**. We will do our best to work through any issues with you and get your code merged into the main branch.
If you found a bug, have questions, or are just having trouble with **bioLEC**, you can:
+ join the **bioLEC User Group on Slack** by sending an email request to: tristan.salles@sydney.edu.au
+ open an issue in our [issue-tracker](https://github.com/Geodels/bioLEC/issues/new) and we'll try to help resolve the concern.
### Where to find support?
Please feel free to submit new issues to the [issue-log](https://github.com/Geodels/bioLEC/issues/new) to request new features, document new bugs, or ask questions.
### License
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the **GNU Lesser General Public License** as published by the **Free Software Foundation**, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
> This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License along with this program. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl-3.0.en.html.
## References
1. E. Bertuzzo, F. Carrara, L. Mari, F. Altermatt, I. Rodriguez-Iturbe & A. Rinaldo - Geomorphic controls on species richness. **PNAS**, 113(7) 1737-1742, [DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1518922113](http://www.pnas.org/content/113/7/1737), 2016.
1. T.R. Etherington - Least-cost modelling and landscape ecology: concepts, applications, and opportunities. Current Landscape Ecology Reports 1:40-53, [DOI: 10.1007/s40823-016-0006-9](https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs40823-016-0006-9), 2016.
1. S. van der Walt , J.L. Schönberger, J. Nunez-Iglesias, F. Boulogne, J.D. Warner, N. Yager, E. Gouillart & T. Yu - Scikit Image Contributors - scikit-image: image processing in Python, [PeerJ 2:e453](https://peerj.com/articles/453/), 2014.
1. T.R. Etherington - Least-cost modelling with Python using scikit-image, [Blog](http://tretherington.blogspot.com/2017/01/least-cost-modelling-with-python-using.html), 2017.




