# Benchmarkit
[](https://badge.fury.io/py/benchmarkit)
[](https://travis-ci.org/vgrabovets/benchmarkit)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/vgrabovets/benchmarkit)
[](https://www.codefactor.io/repository/github/vgrabovets/benchmarkit)
[](https://dependabot.com)
Benchmark and analyze functions' time execution and results over the course of development.
## Features
- No boilerplate code
- Saves history and additional info
- Saves function output and parameters to benchmark data science tasks
- Easy to analyze results
- Disables garbage collector during benchmarking
## Motivation
- I need to benchmark execution time of my function
- I don't want to memorize and write boilerplate code
- I want to compare results with previous runs before some changes were introduced
- I don't want to manually write down results somewhere
- I want to know exact commits of my previous runs months ago
- I want to benchmark accuracy, precision, recall of my models and keep track of hyperparameters
## Installation
```text
pip install benchmarkit
```
## Usage
### Benchmark execution times
Put `@benchmark` decorator over function with piece of code that should be timed
```python
from benchmarkit import benchmark, benchmark_run
N = 10000
seq_list = list(range(N))
seq_set = set(range(N))
SAVE_PATH = '/tmp/benchmark_time.jsonl'
@benchmark(num_iters=100, save_params=True, save_output=False)
def search_in_list(num_items=N):
return num_items - 1 in seq_list
@benchmark(num_iters=100, save_params=True, save_output=False)
def search_in_set(num_items=N):
return num_items - 1 in seq_set
```
- __num_iters__ - how many times to repeat benchmarked function. Default _1_
- __save_params__ - save parameters passed to the benchmarked function in the file with benchmark results. In the example above `num_items` will be saved. Default _False_
- __save_output__ - save benchmarked function output. Should return dict `{'name': value}`. Default _False_. See example how to benchmark model results.
Run benchmark:
```python
benchmark_results = benchmark_run(
[search_in_list, search_in_set],
SAVE_PATH,
comment='initial benchmark search',
rows_limit=10,
extra_fields=['num_items'],
metric='mean_time',
bigger_is_better=False,
)
```
- __functions__ - function or list of functions with `benchmark` decorator
- __save_file__ - path to file where to save results
- __comment__ - comment to save alongside the results
- __rows_limit__ - limit table rows in console output. Default _10_
- __extra_fields__ - extra fields to include in console output
- __metric__ - metric which is used for comparison. Default `mean_time`
- __bigger_is_better__ - whether bigger value of metric indicates that result is better. For time benchmarks should be `False`, for model accuracy should be `True`. Default _False_
Prints to terminal and returns list of dictionaries with data for the last run.
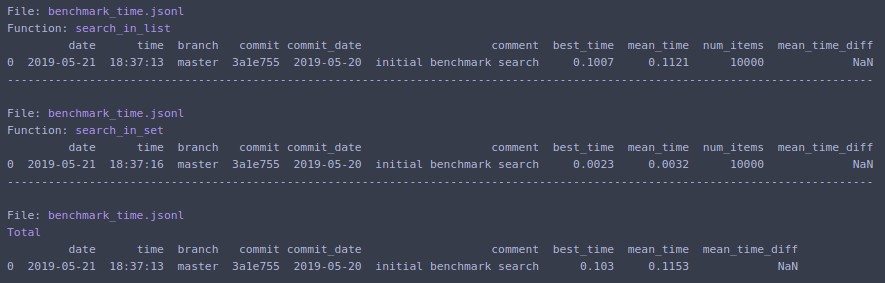
Change `N=1000000` and rerun
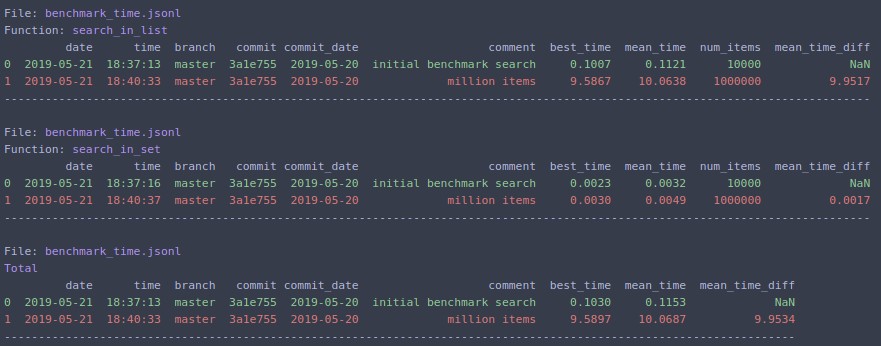
The same can be run from command line:
```text
benchmark_run test_data/time/benchmark_functions.py --save_dir /tmp/ --comment "million items" --extra_fields num_items
```
### Benchmark model results
```python
from benchmarkit import benchmark, benchmark_run
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
MODEL_BENCHMARK_SAVE_FILE = '/tmp/benchmark_model.jsonl'
x, y = load_iris(return_X_y=True)
@benchmark(save_params=True, save_output=True)
def log_regression(C=1.0, fit_intercept=True):
clf = LogisticRegression(
random_state=0,
solver='lbfgs',
multi_class='multinomial',
C=C,
fit_intercept=fit_intercept,
)
clf.fit(x, y)
score = clf.score(x, y)
return {'score': score}
model_benchmark_results = benchmark_run(
log_regression,
MODEL_BENCHMARK_SAVE_FILE,
comment='baseline model',
extra_fields=['C', 'fit_intercept'],
metric='score',
bigger_is_better=True,
)
```

Change hyperparameter `C=0.5` and rerun. Output:
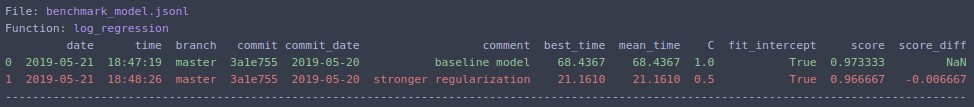
The same can be run from command line:
```text
benchmark_run file_with_benchmark.py --save_dir /tmp/ --comment "stronger regularization" --extra_fields C fit_intercept --metric score --bigger_is_better
```
### Analyze results from the file
```python
from benchmarkit import benchmark_analyze
SAVE_PATH = '/tmp/benchmark_time.jsonl'
benchmark_df = benchmark_analyze(
SAVE_PATH,
func_name=None,
rows_limit=10,
metric='mean_time',
bigger_is_better=False,
extra_fields=['num_items'],
)
```
- __input_path__ - path to `.jsonl` file or directory with `.jsonl` files with benchmark results
- __func_name__ - display statistics for particular function. If `None` then all functions, stored in file, are displayed. Default _None_
- __rows_limit__ - limit table rows in console output. Default _10_
- __metric__ - metric which is used for comparison. Default `mean_time`
- __bigger_is_better__ - whether bigger value of metric indicates that result is better. For time benchmarks should be `False`, for model accuracy should be `True`. Default _False_
- __extra_fields__ - extra fields to include in console output
Prints to terminal and returns pandas `DataFrame`.
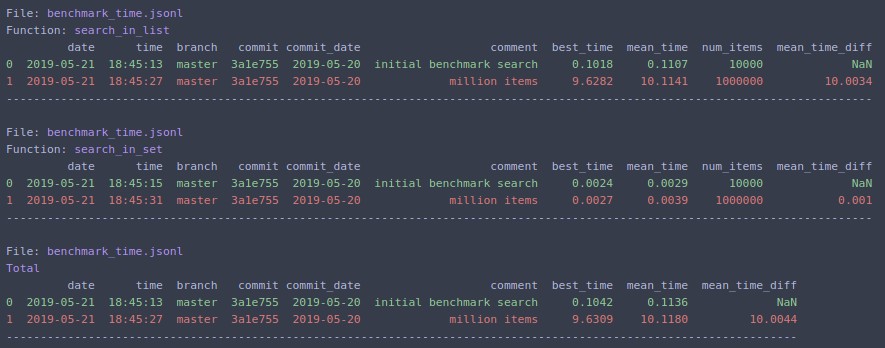
The same can be run from command line:
```text
benchmark_analyze /tmp/benchmark_time.jsonl --extra_fields num_items
```
[Other examples](https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/vgrabovets/benchmarkit/blob/master/notebooks/benchmark_examples.ipynb)




