# Automathon
Created by: Robin Hafid Quintero Lopez
[](https://travis-ci.com/rohaquinlop/automathon)
A Python library for simulating and visualizing finite automata.
## Links
- GitHub repository: https://github.com/rohaquinlop/automathon
- PyPI: https://pypi.org/project/automathon/
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/RobinHafid
- Contact: rohaquinlop301@gmail.com
## Installation
### PyPI
```Python
pip install automathon
```
You also need to install Graphviz on your computer ([download page](https://www.graphviz.org/download/), [installation procedure for Windows](https://forum.graphviz.org/t/new-simplified-installation-procedure-on-windows/224), [archived versions](https://www2.graphviz.org/Archive/stable/)).
Make sure that the directory containing the **dot** executable is on your systems’ path.
## Upgrade
### PyPI
```Python
pip install automathon --upgrade
```
## Deterministic Finite Automata

### Representing the previous automata
```Python
from automathon import DFA
Q = {'q0', 'q1', 'q2'}
sigma = {'0', '1'}
delta = { 'q0' : {'0' : 'q0', '1' : 'q1'},
'q1' : {'0' : 'q2', '1' : 'q0'},
'q2' : {'0' : 'q1', '1' : 'q2'}
}
initialState = 'q0'
F = {'q0'}
automata1 = DFA(Q, sigma, delta, initialState, F)
## This is an example about creating a DFA with the library
```
### Verify if the automata is valid
```python
automata1.isValid() #True
```
### Verify if the automata accept a string
```python
automata1.accept("001001") #True
automata1.accept("00100") #False
```
### Get the automata's complement
```python
notautomata1 = automata1.complement()
notautomata1.accept("00100") #True
```
### Visualize the automata
For both, DFA and NFA, the view method enables to visualize the automaton, receives as parameter a String as the file name for the png and svg files.

```Python
automata1.view("DFA Visualization")
```
### Convert DFA to NFA
If you need to use a DFA and operate with a NFA you can convert your DFA to NFA class, using the function **getNFA**. **getNFA** convert your DFA to NFA class and returns its conversion.
```python
automata1NFA = automata1.getNFA()
automata1NFA.view("DFA to NFA")
```
### Product of two automatas
The **product** function receives a DFA and returns the product of two DFAs, your actual DFA and the given as parameter.
```python
Q = {'A', 'B'}
sigma = {'0', '1'}
delta = {
'A' : {
'0' : 'A',
'1' : 'B'
},
'B' : {
'0' : 'B',
'1' : 'A'
}
}
initialState = 'A'
F = {'B'}
dfa = DFA(Q, sigma, delta, initialState, F)
Q1 = {'R', 'S', 'T', 'U'}
sigma1 = {'0', '1'}
delta1 = {
'R' : {
'0' : 'S',
'1' : 'R'
},
'S' : {
'0' : 'T',
'1' : 'R'
},
'T' : {
'0' : 'U',
'1' : 'R'
},
'U' : {
'0' : 'U',
'1' : 'U'
}
}
initialState1 = 'R'
F1 = {'U'}
dfa1 = DFA(Q1, sigma1, delta1, initialState1, F1)
dfa2 = dfa.product(dfa1)
assert dfa2.isValid() == True
assert dfa2.accept("0001") == True
assert dfa2.accept("00010010") == False
```
### Union of two automatas
The **union** function receives a DFA and returns the union of two DFAs, your actual DFA and the given as parameter.
```python
Q = {'A', 'B'}
sigma = {'0', '1'}
delta = {
'A' : {
'0' : 'A',
'1' : 'B'
},
'B' : {
'0' : 'B',
'1' : 'A'
}
}
initialState = 'A'
F = {'B'}
dfa = DFA(Q, sigma, delta, initialState, F)
Q1 = {'R', 'S', 'T', 'U'}
sigma1 = {'0', '1'}
delta1 = {
'R' : {
'0' : 'S',
'1' : 'R'
},
'S' : {
'0' : 'T',
'1' : 'R'
},
'T' : {
'0' : 'U',
'1' : 'R'
},
'U' : {
'0' : 'U',
'1' : 'U'
}
}
initialState1 = 'R'
F1 = {'U'}
dfa1 = DFA(Q1, sigma1, delta1, initialState1, F1)
dfa2 = dfa.union(dfa1)
assert dfa2.accept("00010010") == True
assert dfa2.accept("0011000") == True
assert dfa.isValid() == True
```
## Non-Deterministic Finite Automata
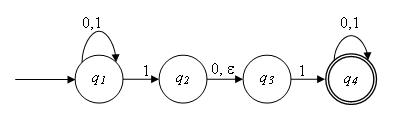
Image taken from: http://www.r9paul.org/blog/2008/nondeterministic-finite-state-machine/
### Representing the previous automata
```Python
from automathon import NFA
## Epsilon Transition is denoted by '' -> Empty string
Q = {'q1', 'q2', 'q3', 'q4'}
sigma = {'0', '1'}
delta = {
'q1' : {
'0' : {'q1'},
'1' : {'q1', 'q2'}
},
'q2' : {
'0' : {'q3'},
'' : {'q3'}
},
'q3' : {
'1' : {'q4'},
},
'q4' : {
'0' : {'q4'},
'1' : {'q4'},
},
}
initialState = 'q1'
F = {'q4'}
automata2 = NFA(Q, sigma, delta, initialState, F)
## This is an example about creating a NFA with the library
```
### Verify if the automata is valid
```python
automata2.isValid() #True
```
### Verify if the automata accept a string
```python
automata2.accept("0000011") #True
automata2.accept("000001") #False
```
### Get the automata's complement
```python
notautomata2 = automata1.complement()
notautomata2.accept("000001") #True
```
### Visualize the automata

```Python
automata2.view("NFA Visualization")
```
### Remove Epsilon transitions from NFA
```python
automata3 = automata2.removeEpsilonTransitions()
automata3.view("NFA without EpsilonTransitions")
```
### Convert NFA to DFA
```python
automata4 = automata3.getDFA()
automata4.view("NFA to DFA")
```
### Product of two automatas
The **product** function receives a NFA and returns the product of two NFAs, your actual NFA and the given as parameter.
```python
Q = {'A', 'B'}
sigma = {'a', 'b'}
delta = {
'A' : {
'a' : {'B'},
'b' : {'A'}
},
'B': {
'a': {'A'},
'b': {'B'}
}
}
initialState = 'A'
F = {'A'}
nfa = NFA(Q, sigma, delta, initialState, F)
Q1 = {'C', 'D'}
sigma1 = {'a', 'b'}
delta1 = {
'C': {
'a' : {'C'},
'b' : {'D'}
},
'D': {
'a' : {'D'},
'b' : {'C'}
}
}
initialState1 = 'C'
F1 = {'C'}
nfa1 = NFA(Q1, sigma1, delta1, initialState1, F1)
nfa2 = nfa.product(nfa1)
assert nfa2.isValid() == True
assert nfa2.accept('') == True
assert nfa2.accept('bb') == True
assert nfa2.accept('b') == False
assert nfa2.accept('bbaa') == True
assert nfa2.accept('bbaaa') == False
```
### Union of two automatas
The **union** function receives a NFA and returns the union of two NFAs, your actual NFA and the given as parameter.
```python
Q = {'A'}
sigma = {'a'}
delta = {
'A' : {
'a' : {'A'}
}
}
initialState = 'A'
F = {'A'}
nfa = NFA(Q, sigma, delta, initialState, F)
Q1 = {'C', 'D', 'E'}
sigma1 = {'a', 'b'}
delta1 = {
'C' : {
'b' : {'D'},
},
'D': {
'a' : {'E'},
'b' : {'D'}
}
}
initialState1 = 'C'
F1 = {'E'}
nfa1 = NFA(Q1, sigma1, delta1, initialState1, F1)
nfa2 = nfa.union(nfa1)
assert nfa2.isValid() == True
assert nfa2.accept("aaaaaa") == True
assert nfa2.accept("aaaabbbbaaa") == False
assert nfa2.accept("bbbbbbbbba") == True
assert nfa2.accept("aaaaaaaab") == False
```
## Errors
Errors that can be returned during the execution, and the cases that can appear.
- **SigmaError**:
- The automata contain an initial state, or a final state that's not defined on Q.
- The automata contain a delta transition that's not defined on Q or in Sigma.
- **InputError**:
- The automata is trying to consume a letter that's not defined in sigma.




