# Action Queues
`actionqueues` is a lightweight way to queue up commands for execution and
rollback on failures.
The idea is that it provides a framework for safely
executing sequences of action with side-effects, like database writes, that
might need later rolling back if later actions fail. In addition, it provides
a standardised way for actions to be retried.
For example, a user sign up process may write to several different systems.
If one system is down, then the other systems modified so far need cleaning
up before the failure is propagated back to the user. Using `actionqueues`
with an action for each external system to be modified enables this pattern,
along with simple retry semantics for likely-transient failures such as network
blips.
## Installing
```
pip install actionqueues
```
## Using Action Queues
It's barebones, the main point is to provide a framework to work within for
actions that have side effects. It's basically the Command pattern, with a
tiny execution framework.
An `Action` is the lowest-level building block. It's any object with `execute`
and `rollback` methods. The `Action` is what handles executing each step of the
overall workflow, and rolling back any changes made to external state. It's
a single object so it can save state for rollback -- for example, primary
keys for any created database rows so they can be deleted during rollback.
The main task of a user of `actionqueues` is to create the `Action` classes
which implement the tasks their workflows require.
Once `Action` classes are written, they can be executed. An `ActionQueue` holds `Actions` for execution and rollback. Add `Action` objects to an `ActionQueue`
for execution. Call `ActionQueue#execute` to start running each action's
`execute` method in the order the `Action` objects were added to the
`ActionQueue`. Behaviour after this point is controlled by the `execute` and
`rollback` methods on the `Action` objects being executed by the queue.
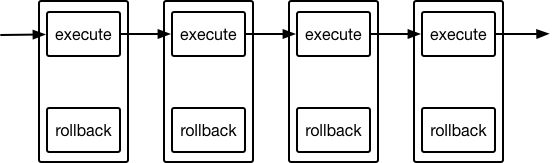
### Normal operation
The default case is that no exception is raised during an `execute` and the
next action in the queue is has `execute` called. This is shown below for a
sequence of `Action` objects within an `ActionQueue`.
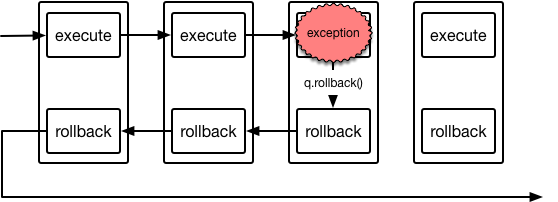
### Exceptions during `execute` cause rollback
If an `Action#execute` raises an exception, the ActionQueue notes where it's
up to in the Actions queued up and then propagates the exception
back up to the caller.
It is then the caller's responsibility to catch the exception and then to call
`ActionQueue#rollback`. This is so the caller can know that the queue of
actions failed and is able to log the exception before calling `rollback`.
Calling `ActionQueue#rollback` will execute the `rollback` method on all
actions where the `execute` method was called, including the one raising the
exception, in the reverse order to that which the `execute` method was called.
Rollback will not be called on actions where `execute` has not been called.
Again, the default case at this point is that `rollback` methods succeed and
don't throw exceptions, leading to each being executed in succession.
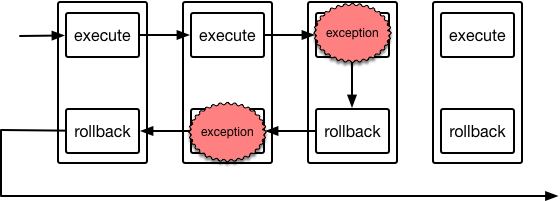
### Exceptions during `rollback`
In contrast to a raised exception from `execute`, if an exception is raised
during the `rollback` method, the `ActionQueue` will
silently swallow the exception and continue executing the `rollback` methods
of earlier `Action` objects in the queue.
This is because, in the rollback scenario, it's most likely that all rollback
actions should happen so the library assumes this. Therefore `rollback` methods
should do their own logging of exceptions before re-raising them.
### Retrying failed operations
There is an exception to the above rules. If the `execute` or `rollback` method
raises a `actionqueue.ActionRetryException` then the `execute` or `rollback`
method will be called again. The `ActionRetryException` init method takes an
optional `ms_backoff` argument to specify a time to sleep before trying the
method again, in milliseconds.
The `ActionQueue` will retry as long as the action keeps raising
`ActionRetryException`, so the action must maintain a retry count
to avoid endless retries. See [below](#retry-exception-helpers) for some
helper classes which cover common cases.
## Example
```python
import random
from actionqueues import actionqueue, action
SUCCEED = 0
RETRY = 1
FAIL = 2
class MyAction(action.Action):
def __init__(self, id):
self._id = id
self._value = 0
def execute(self):
"""Called if actions before it in the queue complete successfully.
Raise any exception to indicate failure.
"""
action = random.choice([SUCCEED, RETRY, FAIL])
if action == RETRY:
print self._id, "Throwing retry exception"
raise actionqueue.ActionRetryException(ms_backoff=0)
elif action == FAIL:
print self._id, "Throwing failure exception"
raise Exception()
else:
print self._id, "Executing success action"
self._value = 1
def rollback(self):
"""Called in reverse order for all actions queued whose execute
method was called when the ActionQueue's rollback method is called.
"""
print self._id, "Rolling back action"
if self._value == 1:
self._value = 0
q = actionqueue.ActionQueue()
q.add(MyAction("a"))
q.add(MyAction("b"))
try:
q.execute()
except:
q.rollback()
```
## Retry exception helpers
It can be tedious to keep track of the backoff and retry count for an action.
Therefore `actionqueues` provides helpers for this called exception factories.
These are created when the `Action` is initialised, and when an `execute`
method hits a retriable exception, it calls the factory's `raise_exception()`
method. In general, this will throw `ActionRetryException` exceptions for a
given number of retries, then throw a generic exception, or one provided by
the `Action` object.
Using separate ExceptionFactory objects for `execute` and `rollback` is usually
required.
The available exception factories are:
- `DoublingBackoffExceptionFactory` which will throw a configurable number
`ActionRetryException` exceptions, each doubling its backoff time.
In this example, the `ZeroDivisionError` will cause 5 retries, at 100, 200,
400, 800 and 1600ms delays, by using a `DoublingBackoffExceptionFactory`:
```python
from actionqueues import actionqueue, action
from actionqueues.exceptionfactory import DoublingBackoffExceptionFactory
class MyFailingAction(action.Action):
def __init__(self):
self._run = 1
self._execute_ex_factory = DoublingBackoffExceptionFactory(
retries=5,
ms_backoff_initial=100
)
self._rollback_ex_factory = DoublingBackoffExceptionFactory(
retries=10,
ms_backoff_initial=100
)
def execute(self):
"""Execute an always failing action, but have it retried 5 times."""
print "Executing action", self._run
self._run += 1
try:
1 / 0
except ZeroDivisionError, ex:
self._execute_ex_factory.raise_exception(original_exception=ex)
def rollback(self):
print "Rollback action", self._run
self._run += 1
try:
1 / 0
except ZeroDivisionError, ex:
self._rollback_ex_factory.raise_exception(original_exception=ex)
q = actionqueue.ActionQueue()
q.add(MyFailingAction())
try:
q.execute()
except:
print "boom"
```




