# Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA) Python package
## In brief
This Python package, `LatentSemanticAnalyzer`, has different functions for computations of
Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA) workflows
(using Sparse matrix Linear Algebra.) The package mirrors
the Mathematica implementation [AAp1].
(There is also a corresponding implementation in R; see [AAp2].)
The package provides:
- Class `LatentSemanticAnalyzer`
- Functions for applying Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) functions on matrix entries
- "Data loader" function for obtaining a `pandas` data frame ~580 abstracts of conference presentations
------
## Installation
To install from GitHub use the shell command:
```shell
python -m pip install git+https://github.com/antononcube/Python-packages.git#egg=LatentSemanticAnalyzer\&subdirectory=LatentSemanticAnalyzer
```
To install from PyPI:
```shell
python -m pip install LatentSemanticAnalyzer
```
-----
## LSA workflows
The scope of the package is to facilitate the creation and execution of the workflows encompassed in this
flow chart:
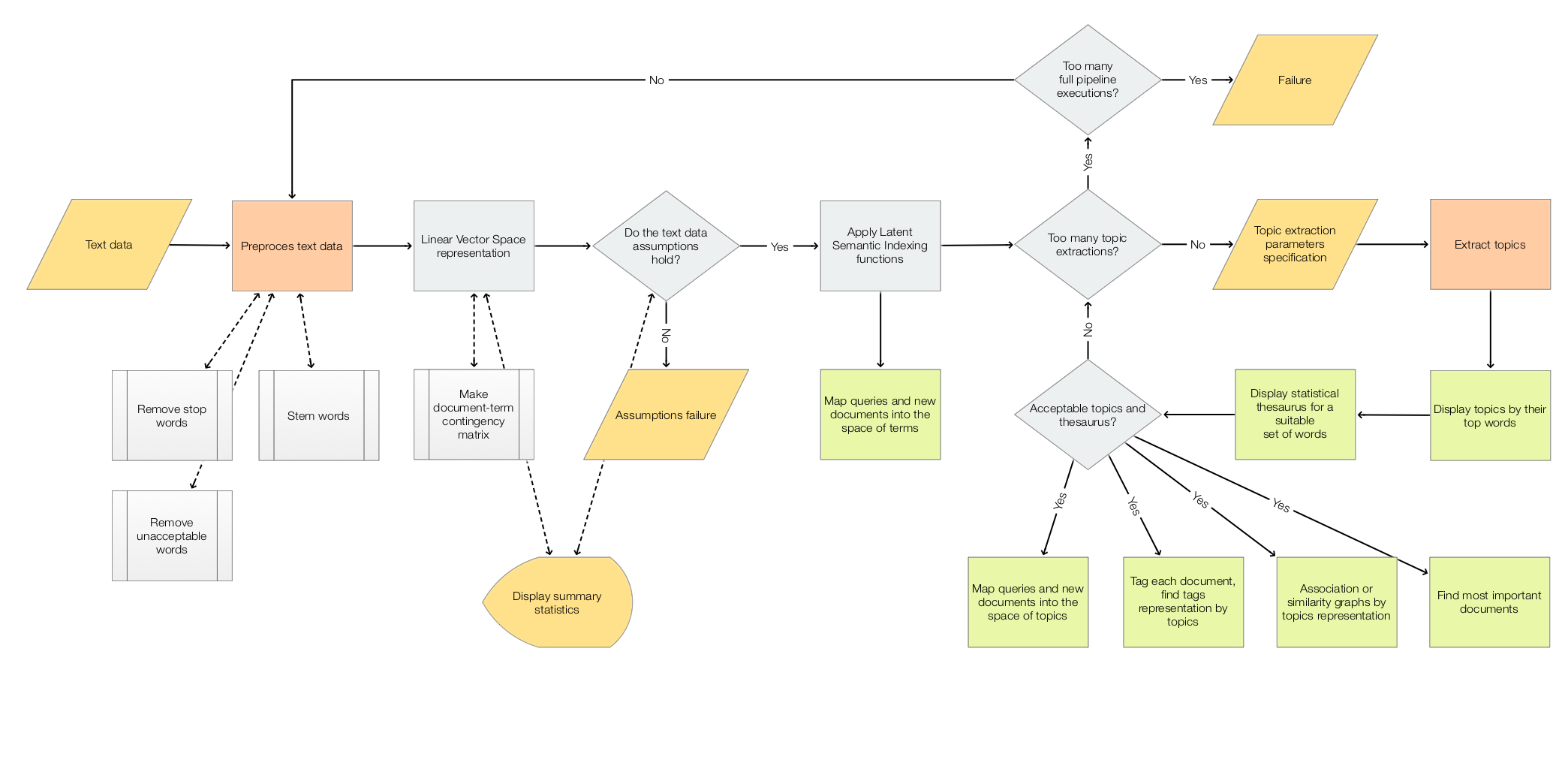
For more details see the article
["A monad for Latent Semantic Analysis workflows"](https://mathematicaforprediction.wordpress.com/2019/09/13/a-monad-for-latent-semantic-analysis-workflows/),
[AA1].
------
## Usage example
Here is an example of a LSA pipeline that:
1. Ingests a collection of texts
2. Makes the corresponding document-term matrix using stemming and removing stop words
3. Extracts 40 topics
4. Shows a table with the extracted topics
5. Shows a table with statistical thesaurus entries for selected words
```
import random
from LatentSemanticAnalyzer.LatentSemanticAnalyzer import *
from LatentSemanticAnalyzer.DataLoaders import *
import snowballstemmer
# Collection of texts
dfAbstracts = load_abstracts_data_frame()
docs = dict(zip(dfAbstracts.ID, dfAbstracts.Abstract))
# Stemmer object (to preprocess words in the pipeline below)
stemmerObj = snowballstemmer.stemmer("english")
# Words to show statistical thesaurus entries for
words = ["notebook", "computational", "function", "neural", "talk", "programming"]
# Reproducible results
random.seed(12)
# LSA pipeline
lsaObj = (LatentSemanticAnalyzer()
.make_document_term_matrix(docs=docs,
stop_words=True,
stemming_rules=True,
min_length=3)
.apply_term_weight_functions(global_weight_func="IDF",
local_weight_func="None",
normalizer_func="Cosine")
.extract_topics(number_of_topics=40, min_number_of_documents_per_term=10, method="NNMF")
.echo_topics_interpretation(number_of_terms=12, wide_form=True)
.echo_statistical_thesaurus(terms=stemmerObj.stemWords(words),
wide_form=True,
number_of_nearest_neighbors=12,
method="cosine",
echo_function=lambda x: print(x.to_string())))
```
------
## Related Python packages
This package is based on the Python package
[`SSparseMatrix`](../SSparseMatrix/README.md), [AAp3]
*TBF...*
------
## Related Mathematica and R packages
### Mathematica
The Python pipeline above corresponds to the following pipeline for the Mathematica package
[AAp1]:
```mathematica
lsaObj =
LSAMonUnit[aAbstracts]⟹
LSAMonMakeDocumentTermMatrix["StemmingRules" -> Automatic, "StopWords" -> Automatic]⟹
LSAMonEchoDocumentTermMatrixStatistics["LogBase" -> 10]⟹
LSAMonApplyTermWeightFunctions["IDF", "None", "Cosine"]⟹
LSAMonExtractTopics["NumberOfTopics" -> 20, Method -> "NNMF", "MaxSteps" -> 16, "MinNumberOfDocumentsPerTerm" -> 20]⟹
LSAMonEchoTopicsTable["NumberOfTerms" -> 10]⟹
LSAMonEchoStatisticalThesaurus["Words" -> Map[WordData[#, "PorterStem"]&, {"notebook", "computational", "function", "neural", "talk", "programming"}]];
```
### R
The package
[`LSAMon-R`](https://github.com/antononcube/R-packages/tree/master/LSAMon-R),
[AAp2], implements a software monad for LSA workflows.
------
## References
### Articles
[AA1] Anton Antonov,
["A monad for Latent Semantic Analysis workflows"](https://mathematicaforprediction.wordpress.com/2019/09/13/a-monad-for-latent-semantic-analysis-workflows/),
(2019),
[MathematicaForPrediction at WordPress](https://mathematicaforprediction.wordpress.com).
### Mathematica and R Packages
[AAp1] Anton Antonov,
[Monadic Latent Semantic Analysis Mathematica package](https://github.com/antononcube/MathematicaForPrediction/blob/master/MonadicProgramming/MonadicLatentSemanticAnalysis.m),
(2017),
[MathematicaForPrediction at GitHub](https://github.com/antononcube/MathematicaForPrediction).
[AAp2] Anton Antonov,
[Latent Semantic Analysis Monad in R](https://github.com/antononcube/R-packages/tree/master/LSAMon-R)
(2019),
[R-packages at GitHub/antononcube](https://github.com/antononcube/R-packages).
### Python packages
[AAp3] Anton Antonov,
[SSparseMatrix Python package](https://pypi.org/project/SSparseMatrix),
(2021),
[PyPI](https://pypi.org).
[AAp4] Anton Antonov,
[SparseMatrixRecommender Python package](https://pypi.org/project/SparseMatrixRecommender),
(2021),
[PyPI](https://pypi.org).
[AAp5] Anton Antonov,
[RandomDataGenerators Python package](https://pypi.org/project/RandomDataGenerators),
(2021),
[PyPI](https://pypi.org).
[AAp6] Anton Antonov,
[RandomMandala Python package](https://pypi.org/project/RandomMandala),
(2021),
[PyPI](https://pypi.org).
[MZp1] Marinka Zitnik and Blaz Zupan,
[Nimfa: A Python Library for Nonnegative Matrix Factorization](https://pypi.org/project/nimfa/),
(2013-2019),
[PyPI](https://pypi.org).
[SDp1] Snowball Developers,
[SnowballStemmer Python package](https://pypi.org/project/snowballstemmer/),
(2013-2021),
[PyPI](https://pypi.org).




