# EVM lab utilities
This package contains various tools to interact with the Ethereum virtual machine.
## Project Structure
| Folder | Description |
| ------------ | ------------- |
| docs | Project documentation |
| evmlab | The evmlab package |
| utilities | Example utilities and proof-of-concepts |
| files | Sample trace files and trace logs |
| output | output directory for artefacts |
| templates | Web application templates (currently used with reproducer) |
| containers | Docker container files |
## Installation
#### From source:
Consider creating a virtualenv.
#> virtualenv -p python3 .env3
#> . .env3/bin/activate
#> python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt
#> python3 setup.py install
#> python3 -m evmlab # verify installation
#### From PIP:
TODO: publish to pip!
#> python3 -m pip install evmlab
#> python3 -m evmlab[consolegui,abidecoder,docker] # verify installation
EVMLab comes with a commandline utility that can be invoked by calling `python3 -m evmlab <subcommand> <args>`
## Compiler
The 'compiler' is a tool to build evm binaries, using a pythonic way to construct the programs using assembly.
Here's an example that tests `ecdsaRecover`:
```python
p = compiler.Program()
p.mstore(0 ,0x38d18acb67d25c8bb9942764b62f18e17054f66a817bd4295423adf9ed98873e)
v = 0x000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001b
p.mstore(32 , v)
p.mstore(64 ,0x723841761d213b60ac1cbf063207cbeba6c2725bcaf7c189e63f13d93fc1dc07)
p.mstore(96 ,0x789d1dd423d25f0772d2748d60f7e4b81bb14d086eba8e8e8efb6dcff8a4ae02)
p.call(0xfff,1,0,0,0x80,0x80,0x20)
p.rreturn(140,20)
code = p.bytecode()
```
Here's an example of stuffing `JUMPDEST` into a program:
```python
p = compiler.Program()
p.jump(0x3)
p.jumpdest()
p.rreturn()
for i in range(0,20000):
p.op(JUMPDEST)
return p.bytecode()
```
## VM
The vm module contais some abstractions to run arbitrary virtual machines, primarily geth `evm` and parity's `parity-evm`.
## Etherchain
The `etherchain` package contains an API for interacting with the Etherchain API.
## Reproduce
An example app is `reproduce.py` which can reproduce an on-chain transaction as a totally local event, and run it in the `evm`.
The app takes a `txhash`, and
1. Fetch the transaction data from an API.
2. Mark (source, destination) as need-to-fetch
3. Fetch balance and nonce at source, add to `genesis`
4. Execute transaction on the `evm`
5. If transaction has any externally reaching ops (BALANCE, EXTCODECOPY, CALL etc),
* Add those accounts as need-to-fetch
6. Go back to 3 until the execution does not result in any more accounts to be fetched.
7. Save the transaction trace and genesis
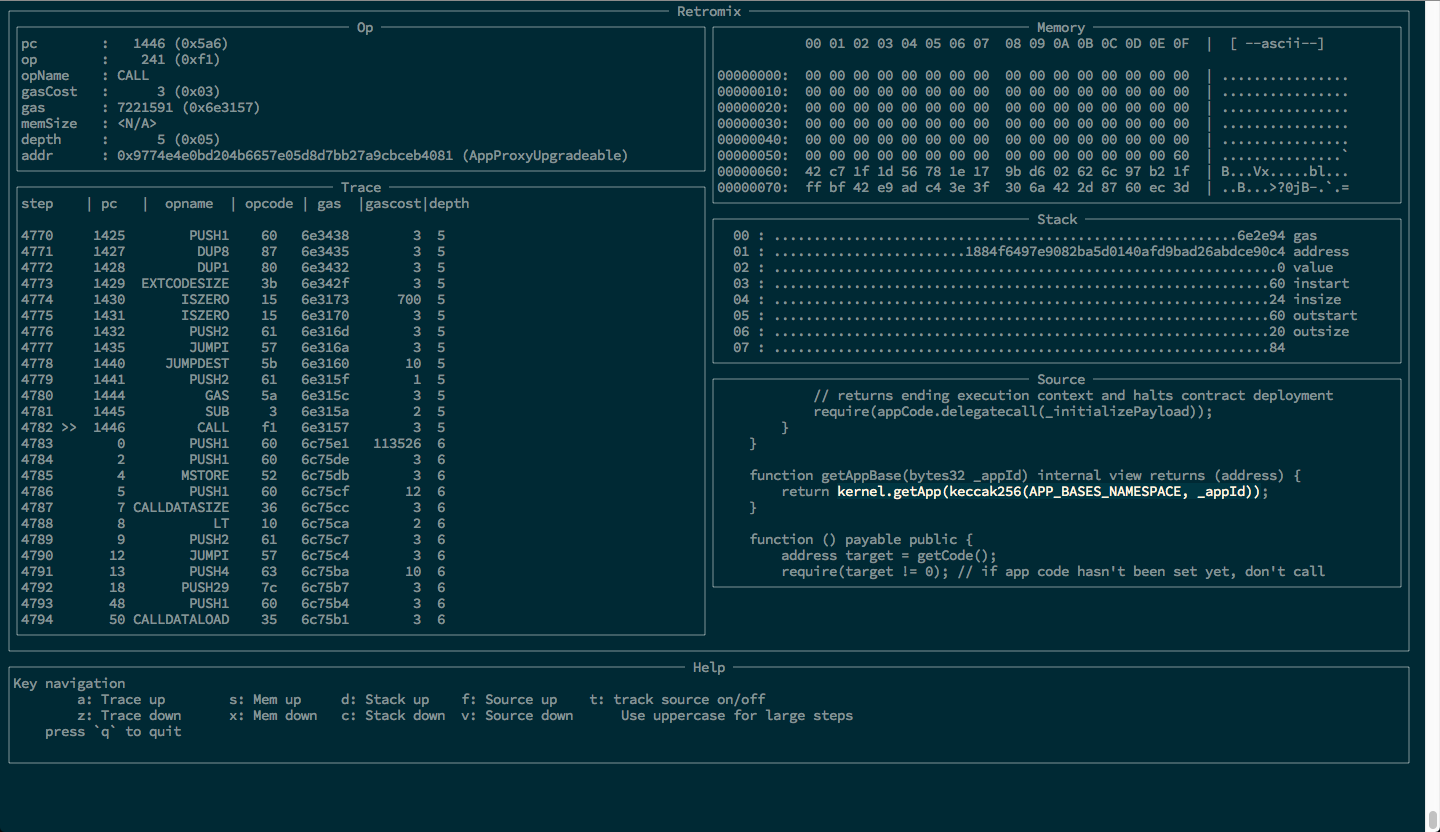
## Opviewer
The 'opviewer.py' is a simple debugger-like trace-viewer. It can be used against an `evm`-trace and navigate the data in a bit more friendly manner than raw json.
Invoke via e.g. `python opviewer.py -f example2.json`
# Running it
The easiest way to get it working is to use a docker image.
```
docker build . -t evmlab && docker run -it evmlab
```
The docker image should also be available at hub.docker.com, as an automated build:
```
docker pull holiman/evmlab && docker run -it holiman/evmlab
```
# EVM
## EVM format
Here's what to think about if you want to add an `evm` to evmlab.
### Input
The `evm` should take the following inputs:
* `--code <code>` - code to be executed.
* `--codeFile <file>` - file containing code to be executed. Sometimes really large chunks of input cannot be passed through bash.
* `--gas <int>`
* `--price <int>`
* `--sender <address>` - address of `ORIGIN`
* `--receiver <address` - address of `ADDRESS`
* `--input <code>` : `CALLDATA`
* `--value <int>`
* `--json` - boolean flag, output json output for each opcode or not (it's useful to disable json when benchmarking)
* `--nomemory` - disable showing the full memory output for each op
* `--create` - if specified, it's executed as initcode
* `--prestate` - a chain specification, the same one that the client normally would use.
Basically, the `evm` should be able to run things very simply, like so:
```bash
$evm --code 6040 --json run
{"pc":0,"op":96,"gas":"0x2540be400","gasCost":"0x3","memory":"0x","memSize":0,"stack":[],"depth":1,"error":null,"opName":"PUSH1"}
{"pc":2,"op":0,"gas":"0x2540be3fd","gasCost":"0x0","memory":"0x","memSize":0,"stack":["0x40"],"depth":1,"error":null,"opName":"STOP"}
{"output":"","gasUsed":"0x3","time":141485}
```
But it should also be able to reconstruct an actual on-chain transaction, with complex options including prestate, where no `code` is passed, since it's already been showed into the `prestate`:
```bash
$evm --prestate /home/martin/workspace/evmlab/output//0xd6d519-genesis-geth_wq38zsy5.json --gas 150000 --sender 0x69ea6b31ef305d6b99bb2d4c9d99456fa108b02a --receiver 0xb97048628db6b661d4c2aa833e95dbe1a905b280 --input a9059cbb0000000000000000000000008eef795fd9150f118bddeca556a5a2a2438ab865000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000081ebd8ffd6b2a58000 --json run
```
### Output
The `evm` should output a `json` object for each operation. Example:
```
{"pc":0,"op":96,"gas":"0x2540be400","gasCost":"0x3","memory":"0x","memSize":0,"stack":[],"depth":1,"error":null,"opName":"PUSH1"}
```
Required: `pc`, `op`, `gas`, `stack`, `depth`
Optional: `opName`, `gasCost`, `error`
The `stack`, `memory` and `memSize` are the values _before_ execution of the op.
At the end of execution, some summarical info is good, e.g.
```
{"output":"","gasUsed":"0x3","time":141485}
```
When errors occur, geth and parity handles them differently.
Minor changes to how things work is ok, we can handle discrepancies in format and minor quirks.




