# Divergence Free Interpolation
Divergence free vector field interpolant for 2D and 3D cases.
Described in [[1]](#1), relies on radial basis functions [[2]](#2).
The current implementation works as expected, but does not scale well,
an improvement would be to implement a multilevel approach [[3]](#3),
but implementing a thinning algorithm [[4]](#4) proved to be challenging.
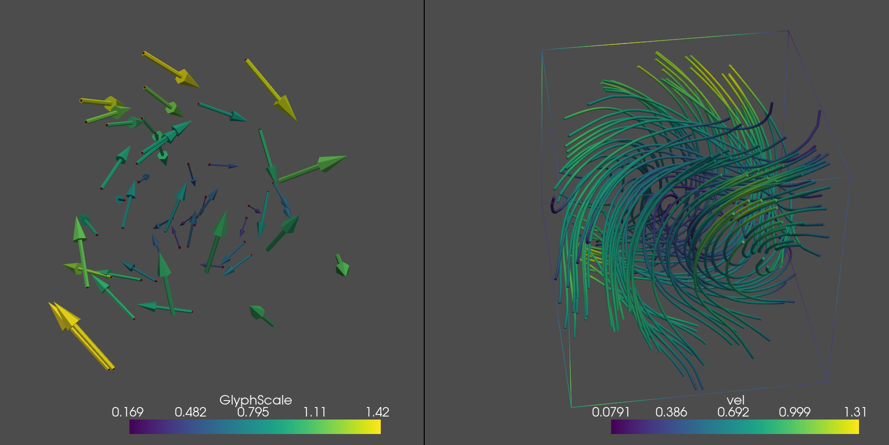
<p align="center">
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Peteris-Zvejnieks/DivergenceFreeInterpolation/main/graphics/2D_sample_field.png" width="400" title="2D vector field">
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Peteris-Zvejnieks/DivergenceFreeInterpolation/main/graphics/2D_interpolated_field.png" width="400">
</p>
## Installation
```bash
pip install Divergence-Free-Interpolant
```
### Test case dependecies
```bash
pip install pyvista matplotlib
```
## Basic functionality
#### Import
```python
import numpy as np
import Divergence_Free_Interpolant as dfi
```
#### Initialize
```python
initialized_interpolant = dfi.interpolant(nu = 5, k = 3, dim = 3)
```
`nu` - Radial basis function parameter: `int`, default value `5`,
in most cases does not have to be changed
`k` - Radial basis function parameter: `int`, default value `3`,
in most cases does not have to be changed
`dim` - Dimensionality of space to interpolate: `int`, default value `3`,
currently only supports `2` and `3`, can be expanded indefinitely.
#### Condition the interpolant
```python
positions = np.random(3, 10)
vectorfield = np.random(3, 10)
initialized_interpolant.condition(positions, vectorfield, support_radius = 0.2, method = 'linsolve')
```
`positions` - vector field coordinates: `np.ndarray`, `shape = (dim, N)`
`vectorfield` - vector field values: `np.ndarray`, `shape = (dim, N)`
`support_radius` - kernel radius: `float`, default value `1`
`method` - method to use for solving the linear system: `str`, default value `linsolve`,
accepts `SVD, penrose, linsolve, lstsq`
#### Interpolate
```python
x, y, z = 0.3, 0.4, 0.6
vector = initialized_interpolant(x, y, z)
```
`x` - x coordinates at which to interpolate: `array_like`
`y` - y coordinates at which to interpolate: `array_like`
`z` - z coordinates at which to interpolate: `array_like`
`vector` - interoplated vector values at the given points: `np.ndarray`, `shape = (..., dim)`
`__call__` is vectorized
if `dim == 2` will not accept the `z` component
See `tests/test_case_2D.py` and `tests/test_case_3D.py` for more detailed examples.
## References
<a id="1">[1]</a> Fuselier, Edward J.
“Sobolev-Type Approximation Rates for Divergence-Free and Curl-Free RBF Interpolants.”
Mathematics of Computation, vol. 77, no. 263, 2008, pp. 1407–23.
http://www.jstor.org/stable/40234564
<a id="2">[2]</a> Wendland, H.
Piecewise polynomial, positive definite and compactly supported radial functions of minimal degree.
Adv Comput Math 4, 389–396 (1995).
https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02123482
<a id="3">[3]</a> Patricio Farrell, Kathryn Gillow, Holger Wendland,
Multilevel interpolation of divergence-free vector fields,
IMA Journal of Numerical Analysis, Volume 37, Issue 1, January 2017, Pages 332–353,
https://doi.org/10.1093/imanum/drw006
<a id="4">[4]</a> Floater M. S. Iske A.
Thinning algorithms for scattered data interpolation .
BIT , 38 , 705 –720 . (1998)




