# CBio-NAMER
**CBioNAMER** (**N**ested n**AM**ed **E**ntity **R**ecognition for **C**hinese **Bio**medical Text) is our method used in [CBLUE](https://tianchi.aliyun.com/dataset/dataDetail?dataId=95414) (Chinese Biomedical Language Understanding Evaluation), a benchmark of Nested Named Entity Recognition. We got the 2nd price of the benchmark by 2021/12/07. Single model CBioNAMER also achieves top20 in CBLUE. The score of CBioNAMER has surpassed human(67.0 in $F_1$).
## Result
Results of our method:
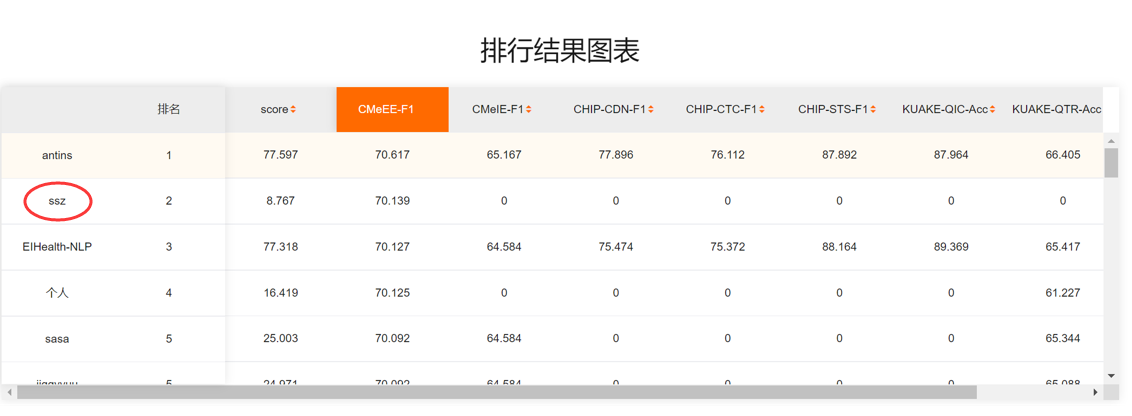
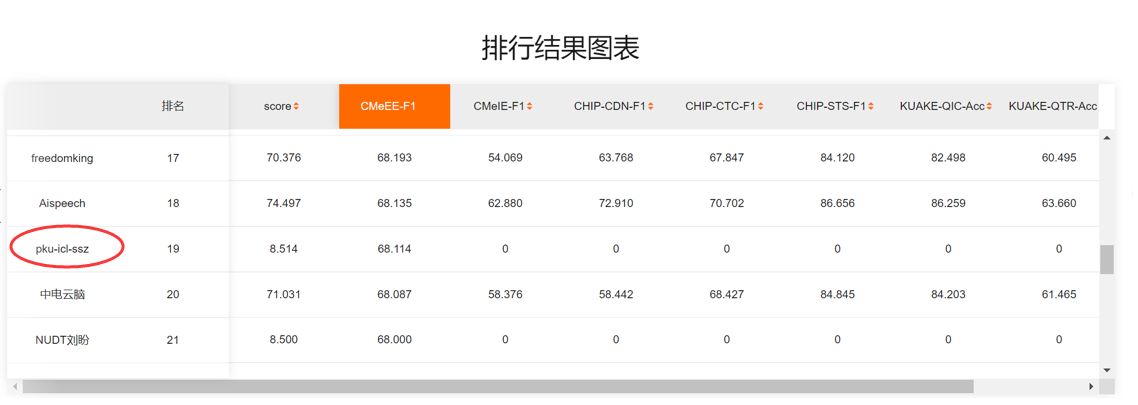
Results of our single model CBioNAMER:
## Approach
CBioNAMER is a sub-model in our result, which is based on [GlobalPointer](https://kexue.fm/archives/8373) (a powerful open-source model, thanks for author, we rewrite it with Pytorch).
## Usage
First, install [PyTorch>=1.7.0](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/). There's no restriction on GPU or CUDA.
Then, install this repo as a Python package:
```bash
$ pip install CBioNAMER
```
Python package `transformers==4.6.1` would be automatically installed as well.
## API
The `CBioNAMER` package provides the following methods:
`CBioNAMER.load_NER(model_save_path='./checkpoint/macbert-large_dict.pth', maxlen=512, c_size=9, id2c=_id2c, c2c=_c2c)`
Returns the pretrained model. It will download the model as necessary. The model would use the first CUDA device if there's any, otherwise using CPU instead.
The `model_save_path` argument specifies the path of the pretrained model weight.
The `maxlen` argument specifies the max length of input sentences. The sentences longer than `maxlen` would be cut off.
The `c_size` argument specifies the number of entity class. Here is `9` for CBLUE.
The `id2c` argument specifies the mapping between id and entity class. By default, the `id2c` argument for CBLUE is:
`_id2c = {0: 'dis', 1: 'sym', 2: 'pro', 3: 'equ', 4: 'dru', 5: 'ite', 6: 'bod', 7: 'dep', 8: 'mic'}`
The `c2c` argument specifies the mapping between entity class and its Chinese meaning. By default, the `c2c` argument for CBLUE is:
`_c2c = {'dis': "疾病", 'sym': "临床表现", 'pro': "医疗程序", 'equ': "医疗设备", 'dru': "药物", 'ite': "医学检验项目", 'bod': "身体", 'dep': "科室", 'mic': "微生物类"}`
------
The model returned by `CBioNAMER.load_NER()` supports the following methods:
`model.recognize(text: str, threshold=0)`
Given a sentence, returns a list of dictionaries with recognized entity, the format of the dictionary is `{'start_idx': entity's starting index, 'end_idx': entity's ending index, 'type': entity class, 'Chinese_type': Chinese meaning of entity class, 'entity': recognized entity}`. The `threshold` argument specifies that the returned list only contains the recognized entity with confidence score higher than `threshold`.
`model.predict_to_file(in_file: str, out_file: str)`
Given input and output `.json` file path, the model would do inference according `in_file`, and the recognized entity would be saved in `out_file`. The output file can be submitted to [CBLUE](https://tianchi.aliyun.com/dataset/dataDetail?dataId=95414). The format of input file is like:
```json
[
{
"text": "该技术的应用使某些遗传病的诊治水平得到显著提高。"
},
...
{
"text": "There is a sentence."
}
]
```
## Examples
```Python
import CBioNAMER
NER = CBioNAMER.load_NER()
in_file = './CMeEE_test.json'
out_file = './CMeEE_test_answer.json'
NER.predict_to_file(in_file, out_file)
```
```python
import CBioNAMER
NER = CBioNAMER.load_NER()
text = "该技术的应用使某些遗传病的诊治水平得到显著提高。"
recognized_entity = NER.recognize(text)
print(recognized_entity)
# output:[{'start_idx': 9, 'end_idx': 11, 'type': 'dis', 'Chinese_type': '疾病', 'entity': '遗传病'}]
```




