
# APIFlask
[](https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask/actions) [](https://codecov.io/gh/apiflask/apiflask)
APIFlask is a lightweight Python web API framework based on [Flask](https://github.com/pallets/flask) and [marshmallow-code](https://github.com/marshmallow-code) projects. It's easy to use, highly customizable, ORM/ODM-agnostic, and 100% compatible with the Flask ecosystem.
With APIFlask, you will have:
- More sugars for view function (`@app.input()`, `@app.output()`, `@app.get()`, `@app.post()` and more)
- Automatic request validation and deserialization
- Automatic response formatting and serialization
- Automatic [OpenAPI Specification](https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification) (OAS, formerly Swagger Specification) document generation
- Automatic interactive API documentation
- API authentication support (with [Flask-HTTPAuth](https://github.com/miguelgrinberg/flask-httpauth))
- Automatic JSON response for HTTP errors
## Requirements
- Python 3.7+
- Flask 1.1.0+
## Installation
For Linux and macOS:
```bash
$ pip3 install apiflask
```
For Windows:
```bash
> pip install apiflask
```
## Links
- Website: <https://apiflask.com>
- Documentation: <https://apiflask.com/docs>
- PyPI Releases: <https://pypi.python.org/pypi/APIFlask>
- Change Log: <https://apiflask.com/changelog>
- Source Code: <https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask>
- Issue Tracker: <https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask/issues>
- Discussion: <https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask/discussions>
- Twitter: <https://twitter.com/apiflask>
## Example
```python
from apiflask import APIFlask, Schema, abort
from apiflask.fields import Integer, String
from apiflask.validators import Length, OneOf
app = APIFlask(__name__)
pets = [
{'id': 0, 'name': 'Kitty', 'category': 'cat'},
{'id': 1, 'name': 'Coco', 'category': 'dog'}
]
class PetIn(Schema):
name = String(required=True, validate=Length(0, 10))
category = String(required=True, validate=OneOf(['dog', 'cat']))
class PetOut(Schema):
id = Integer()
name = String()
category = String()
@app.get('/')
def say_hello():
# returning a dict or list equals to use jsonify()
return {'message': 'Hello!'}
@app.get('/pets/<int:pet_id>')
@app.output(PetOut)
def get_pet(pet_id):
if pet_id > len(pets) - 1:
abort(404)
# you can also return an ORM/ODM model class instance directly
# APIFlask will serialize the object into JSON format
return pets[pet_id]
@app.patch('/pets/<int:pet_id>')
@app.input(PetIn(partial=True))
@app.output(PetOut)
def update_pet(pet_id, data):
# the validated and parsed input data will
# be injected into the view function as a dict
if pet_id > len(pets) - 1:
abort(404)
for attr, value in data.items():
pets[pet_id][attr] = value
return pets[pet_id]
```
<details>
<summary>You can also use class-based views based on <code>MethodView</code></summary>
```python
from apiflask import APIFlask, Schema, abort
from apiflask.fields import Integer, String
from apiflask.validators import Length, OneOf
from flask.views import MethodView
app = APIFlask(__name__)
pets = [
{'id': 0, 'name': 'Kitty', 'category': 'cat'},
{'id': 1, 'name': 'Coco', 'category': 'dog'}
]
class PetIn(Schema):
name = String(required=True, validate=Length(0, 10))
category = String(required=True, validate=OneOf(['dog', 'cat']))
class PetOut(Schema):
id = Integer()
name = String()
category = String()
class Hello(MethodView):
# use HTTP method name as class method name
def get(self):
return {'message': 'Hello!'}
class Pet(MethodView):
@app.output(PetOut)
def get(self, pet_id):
"""Get a pet"""
if pet_id > len(pets) - 1:
abort(404)
return pets[pet_id]
@app.input(PetIn(partial=True))
@app.output(PetOut)
def patch(self, pet_id, data):
"""Update a pet"""
if pet_id > len(pets) - 1:
abort(404)
for attr, value in data.items():
pets[pet_id][attr] = value
return pets[pet_id]
app.add_url_rule('/', view_func=Hello.as_view('hello'))
app.add_url_rule('/pets/<int:pet_id>', view_func=Pet.as_view('pet'))
```
</details>
<details>
<summary>Or use <code>async def</code> with Flask 2.0</summary>
```bash
$ pip install -U flask[async]
```
```python
import asyncio
from apiflask import APIFlask
app = APIFlask(__name__)
@app.get('/')
async def say_hello():
await asyncio.sleep(1)
return {'message': 'Hello!'}
```
See <em><a href="https://flask.palletsprojects.com/async-await">Using async and await</a></em> for the details of the async support in Flask 2.0.
</details>
Save this as `app.py`, then run it with :
```bash
$ flask run --reload
```
Now visit the interactive API documentation (Swagger UI) at <http://localhost:5000/docs>:
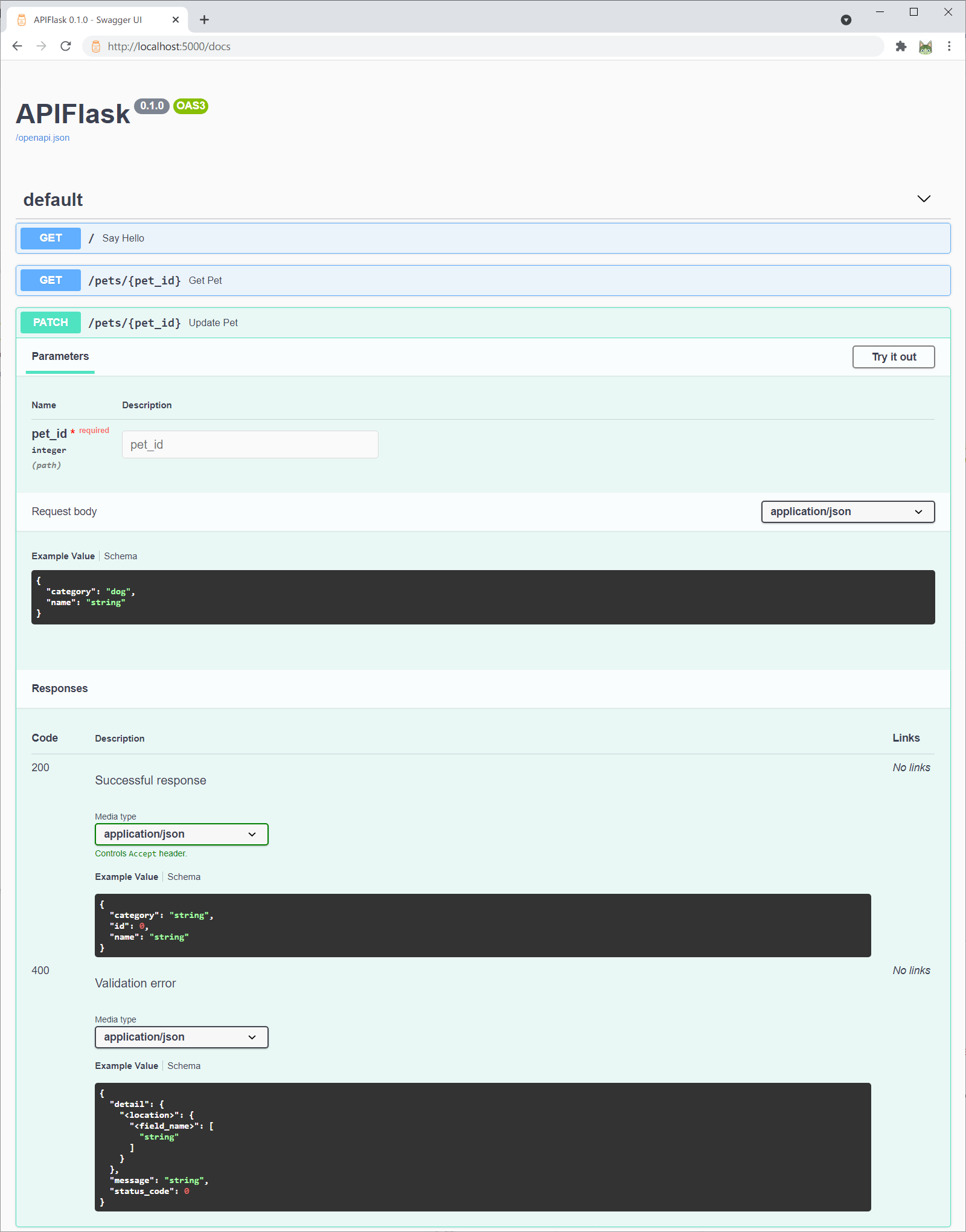
Or you can change the API documentation UI when creating the APIFlask instance with the `docs_ui` parameter:
```py
app = APIFlask(__name__, docs_ui='redoc')
```
Now <http://localhost:5000/docs> will render the API documentation with Redoc.
Supported `docs_ui` values (UI libraries) include:
- `swagger-ui` (default value): [Swagger UI](https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui)
- `redoc`: [Redoc](https://github.com/Redocly/redoc)
- `elements`: [Elements](https://github.com/stoplightio/elements)
- `rapidoc`: [RapiDoc](https://github.com/rapi-doc/RapiDoc)
- `rapipdf`: [RapiPDF](https://github.com/mrin9/RapiPdf)
The auto-generated OpenAPI spec file is available at <http://localhost:5000/openapi.json>. You can also get the spec with [the `flask spec` command](https://apiflask.com/openapi/#the-flask-spec-command):
```bash
$ flask spec
```
For some complete examples, see [/examples](https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask/tree/main/examples).
## Relationship with Flask
APIFlask is a thin wrapper on top of Flask. You only need to remember the following differences (see *[Migrating from Flask](https://apiflask.com/migrating)* for more details):
- When creating an application instance, use `APIFlask` instead of `Flask`.
- When creating a blueprint instance, use `APIBlueprint` instead of `Blueprint`.
- The `abort()` function from APIFlask (`apiflask.abort`) returns JSON error response.
For a minimal Flask application:
```python
from flask import Flask, request, escape
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello():
name = request.args.get('name', 'Human')
return f'Hello, {escape(name)}'
```
Now change to APIFlask:
```python
from apiflask import APIFlask # step one
from flask import request, escape
app = APIFlask(__name__) # step two
@app.route('/')
def hello():
name = request.args.get('name', 'Human')
return f'Hello, {escape(name)}'
```
In a word, to make Web API development in Flask more easily, APIFlask provides `APIFlask` and `APIBlueprint` to extend Flask's `Flask` and `Blueprint` objects and it also ships with some helpful utilities. Other than that, you are actually using Flask.
## Relationship with marshmallow
APIFlask accepts marshmallow schema as data schema, uses webargs to validate the request data against the schema, and uses apispec to generate the OpenAPI representation from the schema.
You can build marshmallow schemas just like before, but APIFlask also exposes some marshmallow APIs for convenience (it's optional, you can still import everything from marshamallow directly):
- `apiflask.Schema`: The base marshmallow schema class.
- `apiflask.fields`: The marshmallow fields, contain the fields from both marshmallow and Flask-Marshmallow. Beware that the aliases (`Url`, `Str`, `Int`, `Bool`, etc.) were removed.
- `apiflask.validators`: The marshmallow validators.
```python
from apiflask import Schema
from apiflask.fields import Integer, String
from apiflask.validators import Length, OneOf
from marshmallow import pre_load, post_dump, ValidationError
```
## Credits
APIFlask starts as a fork of [APIFairy](https://github.com/miguelgrinberg/APIFairy) and is inspired by [flask-smorest](https://github.com/marshmallow-code/flask-smorest) and [FastAPI](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi) (see *[Comparison and Motivations](https://apiflask.com/comparison)* for the comparison between these projects).




